|
Anatomy
of a GMC DUKW GMC at War
General Motors Truck and Coach Division of General Motors Corporation
During World
War Two
Pontiac, MI
1911-Present
This page updated 2-8-2025.
At the beginning of World War Two, what later
became the GMC Truck and Bus Division of General Motors, was part of the
Yellow Truck and Coach Manufacturing Company. Yellow Truck had
originally formed in 1923 as a subsidiary of Yellow Cab and was
originally named the Yellow Coach Manufacturing Company. GM and
Yellow Truck merged on July 8, 1925, with General Motors owning 60% by
using the assets of GMC in the new holding company. The new
company was known as Yellow Truck and Coach Manufacturing Company.
GM made the purchase in order manufacture buses. A purchase of 160
acres near Pontiac, MI led to the construction of the world's largest
truck plant, with 26
acres under roof. Production began at the new plant in January
1928.
The General Motors truck operation that became
part of the new holding company in 1925 had its roots in two
independent Detroit truck manufacturers that were purchased by WC Durant
for his auto empire. Reliance Motor Company was purchased in 1908
and Rapid Motor Vehicle Company in 1909, resulting in the General Motors
Truck Company (GMC) in 1911.
In September 1943 General Motors purchased all
of the assets of the Yellow Truck and Coach Manufacturing Company and
created the General Motors Truck and Bus Division which has evolved into
the GMC of today. Today its product line is upscale SUVs and
pickup trucks, as it shed the heavy duty truck and bus business in the
late 20th century.
Early in World War Two, the trucks that Yellow Truck and Coach
Manufacturing Company produced were officially identified by the
military as being built by that company even though they were known by
to the public as GMC, or to the GIs as "Jimmies." After 1943, they
were identified as GMC products by the military. In this webpage,
the name GMC will be used for all of the vehicles built at the Pontiac
truck plant by the future GMC division.
Many persons refer not only the 2-1/2 ton 6x6
trucks built by GMC, but International Harvester and Studebaker during
World War Two as "deuce and a halves." In my research, I have yet
to find a World War Two document that describes the trucks in this
manner. It is my contention that this is a post-World War Two term, most likely originating
in the Vietnam War era.

The GMC Division of General Motors won the
Army-Navy "E" for Excellence Award two times.
GMC World War Two Products:
GMC had
$2,017,518,000 in major contracts during World War Two. There were
571,053 trucks produced with the GMC nameplate ranging in size from 1-1/2-ton to
10-ton in capacity during World War Two.
Between 1940 and 1945 GMC built 546,020
2-1/2-ton 6x6 trucks including 21,147 of the amphibious DUKW.
Another 7,232 were cab-over-engine 2-1/2-ton 6x6 trucks with either
15-foot or 17-foot cargo beds. The remaining 517,641 trucks were
the CCKW-352 and CCKW-353 types. GMC built 362,348, or 70% of these, at its
Pontiac, MI plant. Chevrolet built the other 155,293 at two of its
assembly plants.
There were 21,147 2-1/2 ton 6x6 amphibious trucks produced with the
GMC nameplate on it. GMC built 14,399, or 68% of these at its
Pontiac, MI plant. Chevrolet built the other 6,748 at its St.
Louis assembly plant.
The rest of the various types of trucks, buses
and trailers were all built in the GMC Pontiac, MI plant.
GMC also built 2,249 buses, 30 T18E2 Boarhound Armored Cars, and 6
trailers during 1940-1945.
GMC also buillt an unknown number of M18 Hellcat tank
Destroyer hulls. The Buick Motor Division built 2,507 M18s during
World War Two. Fisher Body is documented to have provided Buick
with 1,511 hulls. There is no documentation as to how many hulls
GMC built, but there are photos of the GM division building them. If
GMC and Fisher Body built all of the hulls, GMC would have provided 996
for the war effort.
|
GMC
World War Two Trucks Accepted by Detroit Ordnance, US Army
The information below comes from "Summary Report of
Acceptances, Tank-Automotive Material, 1940-1945"
Published by Army Services Forces, Office, Chief of
Ordnance-Detroit, Production Division, Requirements and
Progress Branch
January 21, 1946. |
|
Type |
GMC Model |
1940 |
1941 |
1942 |
1943 |
1944 |
1945 |
Total |
| 1-1/2-ton 4x2 Cargo wo/w |
CC-302 |
39 |
|
8 |
|
|
|
47 |
|
1-1/2-ton 4x2 Communication K-18 |
CC-302 |
47 |
258 |
109 |
|
|
|
414 |
| 1-1/2-ton 4x2 Dump wo/w |
CC-302, ACX-353 |
16 |
|
3 |
|
|
|
19 |
| 1-1/2-ton 4x2 Panel Delivery |
AF-312 |
18 |
|
|
|
|
|
18 |
| 1-1/2-ton 4x2 Platform w/ Elevator |
CC-252 |
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
1 |
| 1-1/2-ton 4x2 Wrecker |
ACKWX-353 |
23 |
|
|
|
|
|
23 |
| Total
1-1/2-ton 4x2 |
|
143 |
258 |
121 |
|
|
|
522 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Total 1-1/2-3 ton 4x4 Chassis |
? |
|
|
49 |
|
|
|
49 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 2-1/2-ton 6x6
Amphibian |
DUKW-353 |
|
|
235 |
4508 |
11,316 |
5,088 |
21,147 |
| 2-1/2 ton 6x6 Bomb Services Chassis M27,
M27B1 |
CCKW-353 |
|
|
|
|
|
627 |
627 |
| 2-1/2 ton 6x6 Cargo wo/w |
CCKW-353 |
6,550 |
22,459 |
43,935 |
58,448 |
53,422 |
46,538 |
231,352 |
| 2-1/2 ton 6x6 Cargo w/w |
CCKW-353 |
1,202 |
7,564 |
27,795 |
27,870 |
32,221 |
24,019 |
120,671 |
| 2-1/2 ton 6x6 Cargo 15-Foot Body |
AFKWX-353 |
|
|
613 |
1,619 |
|
|
2,232 |
| 2-1/2 ton 6x6 Cargo 17-Foot Body |
AFKWX-353 |
|
|
|
|
4,000 |
1,000 |
5,000 |
| 2-1/2 ton 6x6 Cargo SWB wo/w |
CCKW-352 |
244 |
11,862 |
14,110 |
5,380 |
|
|
31,596 |
| 2-1/2 ton 6x6 Cargo SWB w/w |
CCKW-352 |
|
8,508 |
8,547 |
3,145 |
954 |
440 |
21,594 |
| 2-1/2 ton 6x6 Chassis wo/w |
CCKW-353 |
36 |
124 |
15,535 |
18,145 |
11,279 |
1,641 |
46,760 |
| 2-1/2 ton 6x6 Chassis w/w |
CCKW-353 |
|
|
237 |
3,321 |
2,674 |
4,184 |
10,416 |
| 2-1/2 ton 6x6 Chassis SWB wo/w |
CCKW-352 |
|
2 |
|
800 |
|
|
802 |
| 2-1/2 ton 6x6 Dump wo/w |
CCKW-353 |
|
1 |
|
1,300 |
|
|
1,301 |
| 2-1/2 ton 6x6 Dump w/w |
CCKW-353 |
|
|
|
10,905 |
23,639 |
12,500 |
47,044 |
| 2-1/2 ton 6x6 Stock Rack, 15-foot Body |
CCKW-353 |
27 |
93 |
|
|
|
|
120 |
| 2-1/2 ton 6x6 Tank 750 Gal. Gas (Complete
Units) |
CCKW-353 |
114 |
183 |
750 |
642 |
2,282 |
162 |
4,133 |
| 2-1/2 ton 6x6 Tank 750 Gal. Water |
CCKW-353 |
|
|
60 |
887 |
215 |
46 |
1,208 |
| 2-1/2 ton 6x6 Van |
CCKW-353 |
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
1 |
| 2-1/2 ton 6x6 Battery Servicing |
CCKW-353 |
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
8 |
| 2-1/2 ton 6x6 Fuel Servicing |
CCKW-353 |
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
8 |
| Total
2-1/2 ton 6x6 |
|
8,173 |
50,796 |
111,834 |
136,970 |
142,002 |
96,245 |
546,020 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Total 2-1/2 ton 6x4 Cargo wo/w |
CCW-353 |
|
707 |
22,687 |
255 |
|
|
23,649 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 2-1/2 ton 4x4 Tire Servicing |
ACK-353 |
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
5 |
| 2-1/2 ton 4x4 Tractor COE |
AFKX-502 |
81 |
|
|
|
|
|
81 |
| Total
2-1/2 ton 4x4 COE |
|
81 |
|
5 |
|
|
|
86 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 2-1/2 ton 4x2 Canopy Express |
CC-453 |
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
1 |
| 2-1/2 ton 4x2 Cargo |
CC-453 |
109 |
9 |
|
|
|
|
118 |
| 2-1/2 ton 4x2 Dump |
CCX-453, ACX-453 |
110 |
19 |
|
|
|
|
129 |
| 2-1/2 ton 4x2 Stake and Platform |
CC-453 |
22 |
4 |
18 |
|
|
|
44 |
| 2-1/2 ton 4x2 Tractor |
ACX-503 |
8 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
10 |
| Total
2-1/2 ton 4x2 |
|
249 |
35 |
18 |
|
|
|
302 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 4-ton 4x4 Cargo |
AFKX-804 |
11 |
|
|
|
|
|
11 |
| 4-ton 4x4 Van |
AFKX-804 |
|
192 |
124 |
|
|
|
316 |
| Total
4-ton 4x4 |
|
11 |
192 |
124 |
|
|
|
327 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 5-ton 4x2 Dump |
AC-803 |
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
12 |
| 5-ton 4x2 Stake and Platform |
AC-805 |
6 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
7 |
| Total
5-ton 4x2 |
|
18 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
19 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Total 8-ton 6x4 Tractor |
ACK-853 |
|
11 |
|
|
|
|
11 |
| Total 10-ton 4x2 COE |
? |
|
50 |
|
|
|
|
50 |
| Total Tractor Truck -
to be used with Semi-Trailer Tank |
? |
|
|
18 |
|
|
|
18 |
| Truck Totals |
|
8,675 |
52,050 |
134,856 |
137,225 |
142,002 |
96,245 |
571,053 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Bus 25-29 Passenger |
? |
|
6 |
5 |
|
|
|
11 |
| 1-1/2-3 ton 4x4 Bus Body |
? |
276 |
974 |
938 |
|
|
|
2,188 |
| Bus 37 Passenger 4x2 Integral Intra-City Type |
? |
|
|
|
|
|
40 |
40 |
| Bus 32 Passenger 4x2 Integral Inter-City Type |
? |
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
10 |
| Bus Totals |
|
276 |
980 |
943 |
|
|
50 |
2,249 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Total Trailer 3-1/2-ton 2W 16 foot Stake and
Platform |
? |
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
GMC
World War Two Armored Cars Accepted by Detroit Ordnance, US Army
The information below comes from "Summary Report of
Acceptances, Tank-Automotive Material, 1940-1945"
Published by Army Services Forces, Office, Chief of
Ordnance-Detroit, Production Division, Requirements and
Progress Branch
January 21, 1946. |
|
Type |
GMC Model |
1940 |
1941 |
1942 |
1943 |
1944 |
1945 |
Total |
| Car Armored Heavy
T18E2 |
? |
|
|
2 |
28 |
|
|
30 |
Author's Note
and Disclaimer: The Detroit Office
of Ordnance of the U.S. Army was the primary purchasing entity for
vehicles for the U.S. Army during WWII. It also purchased vehicles
for the USMC, US Navy, and for Lend-Lease. However, there were
other organizations that also purchased vehicles including the Army
Corps of Engineers, U.S. Army Air Force, U.S. Army Signal Corps, Navy
Bureau of Ordnance, Navy Bureau of Aeronautics, and foreign countries
making direct purchases.
A note on Chevrolet CCKW and DUKW
production: Some authors state that GMC took over management
of Chevrolet plants. This is not true. Chevrolet maintained
control of both the Baltimore and St. Louis assembly plants that built
GMC products. Because Chevrolet was a subcontractor to GMC, the
trucks had GMC data plates in them.
At the end of the war, all CCKW production had
shifted to Chevrolet St. Louis. In 1944 and 1945, the daily run rate for CCKWs
was larger at St. Louis than at the GMC plant in Pontiac, MI.
Therefore, while all of the nameplates on the CCKWs are GMC, if the
truck was built in 1944 or 1945, there is a greater than 50% chance that
it is the Chevrolet-built version. All CCKWs built in St. Louis, with
the exception of the last (1,000) units, had Chevrolet axles on them.
Time
line for the CCKW:
Mid 1941: Part number 1608 cab (Chevrolet manufactured item) introduced
with the mirror
mounted to the cowl rather than on the door hinge, flat panel instrument
cluster.
Mid 1941: Part number 1609 cab (Chevrolet manufactured item) same
as 1608 but with hatch for gunner.
August 1942 through the spring of 1943: Part number 1619 soft top
cabs introduced replacing the all steel cab part numbers 1608 and 1609.
October 1942: Four spoke wooden rim steering wheel
introduced.
Axles: GMC used two types of axles for
its trucks. Originally a Timken-Detroit Axle Company split differential type was used.
However, Timken-Detroit, for various reasons, was not able to keep up with the
demand. Chevrolet front face differentials were substituted.
A Notable Quote:
For the United States,
World War Two was the first completely mechanized war. There were
tanks, jeeps, tanks, armored cars, tank destroyers, halftracks, and
trucks that were used by the U.S. military. They came in all sizes
from the 1/4 ton 4x4 Jeep to the 10 ton wrecker. But there is one
truck that comes to a person's mind when thinking of trucks from World
War Two, and it is the GMC 2-1/2-ton 6X6. It is the definitive
truck of World War Two!
A quote from "The Great Crusade" by General
Dwight D. Eisenhower: "Incidentally, four other pieces of
equipment that most senior officers came to regard as among the most
vital to our success in Africa and Europe were the bulldozer, the jeep,
the 2-1/2-ton truck, and the C-47 airplane."
For the United States Army in Africa and Europe, the 2-1/2-ton truck
General Eisenhower refers to is the GMC CCKW. The CCKW was
exclusively used by the Army, as the Studebaker version went to Great
Britain and Russia, and the International Harvester version was also
sent overseas on Lend-Lease or were used by the U.S. Marines and Navy.
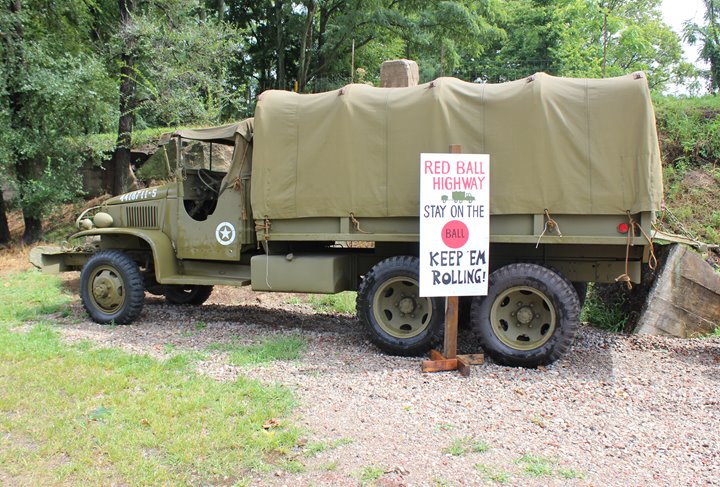

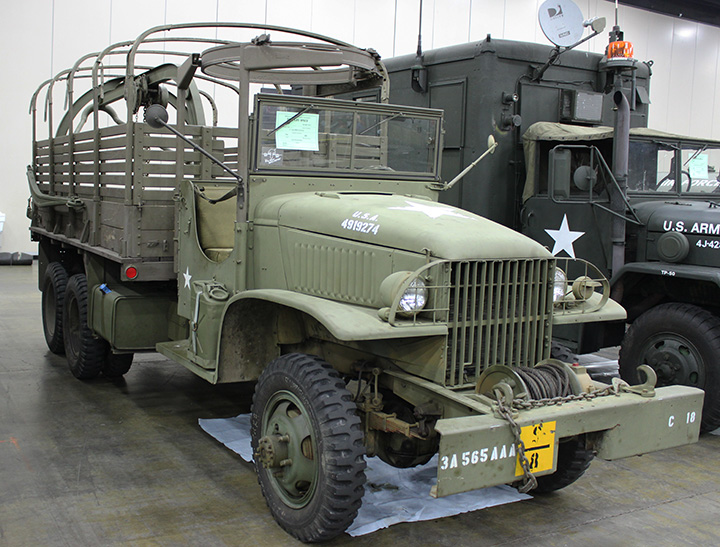
This is what comes to mind when one thinks
of the WWII truck. The GMC 2-1/2 ton CCKW-353 6x6 truck noted by
General Eisenhower in his book. Author's photo.

A
GMC 2-1/2 ton 6x6, or "Jimmy", as they were known to the troops during
World War Two, running the Red Ball Express and keeping the front line troops
supplied with beans, bullets, and bandages! This is a CCKW-353 long
bed with a hard cab, indicating it was built no later than the spring of
1943.
The CCW: C = 1941 design,
C = Standard cab,
W= Tandem rear wheels
The CCW was the
same at the CCKW but was a 6x4, as the K in the CCKW designation denotes
all-wheel drive. 23,649 were built between 1941 and 1943.
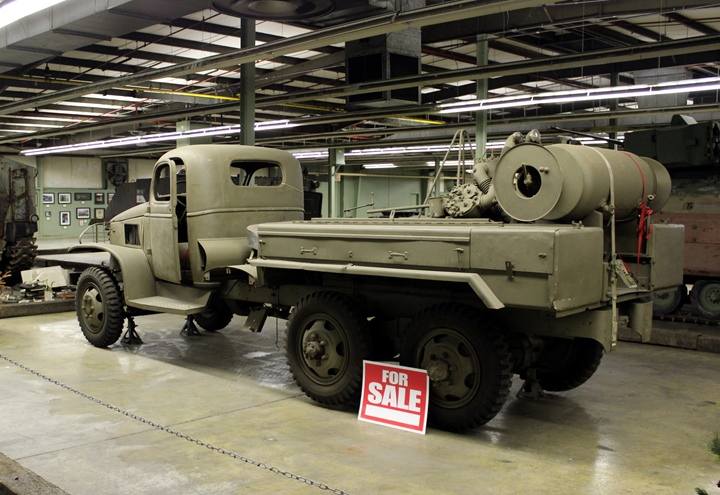

This GMC 1941-1942 CCW 6x4 was photographed
at the AAF Tank Museum minus its outer back wheels. This particular
example has a 210 CFM Roi Air Compressor mounted on the bed.
Author's photo.
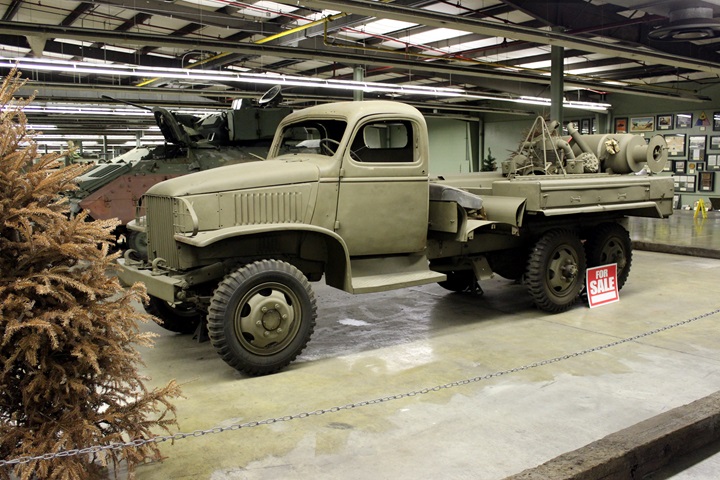

The Museum has the CCW misidentified as a
1944 CCKW. Starting in August 1942 through spring of 1943, the
hardtops were replaced by soft
top cabs. Also, GMC only ran the 6x4 CCW from late 1941 to late summer of
1942. During this period, 23,501 were built and shipped overseas
under Lend-Lease. Author's photo.
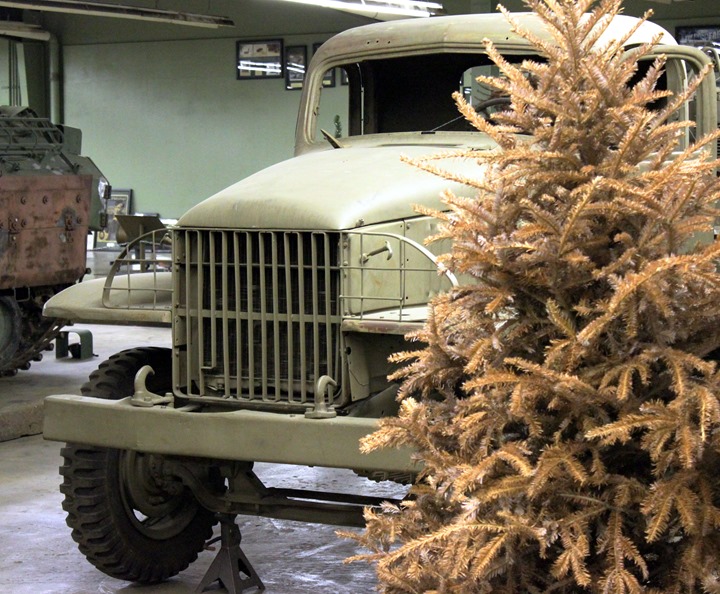

The GMC has a straight front axle with no
differential, making it 6x4 and identifying it as a CCW. The GMC version of the 6x4 went to China and the Studebaker
6x4 went to Russia. Author's photo.
The CCKW: C = 1941 design,
C = Standard cab,
K = All wheel drive,
W= Tandem rear wheels
The CCKW was built as
either
the CCKW-352 short bed and the CCKW-353 twelve foot long bed with a multitude of bed types.
CCKW-352:
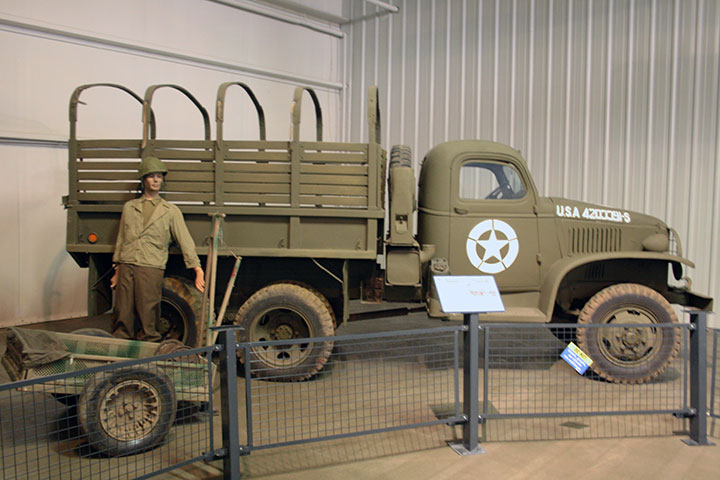

This is a pre mid-1941 CCKW-352 short bed without a
winch. There is no bracket on the cowling for a mirror; and the
spare tires and fuel tank are
directly behind the cab. One of the uses for the CCKW-352 was as a
prime mover for artillery, and to carry the gun crew in the bed of the
truck.
Author's photo.
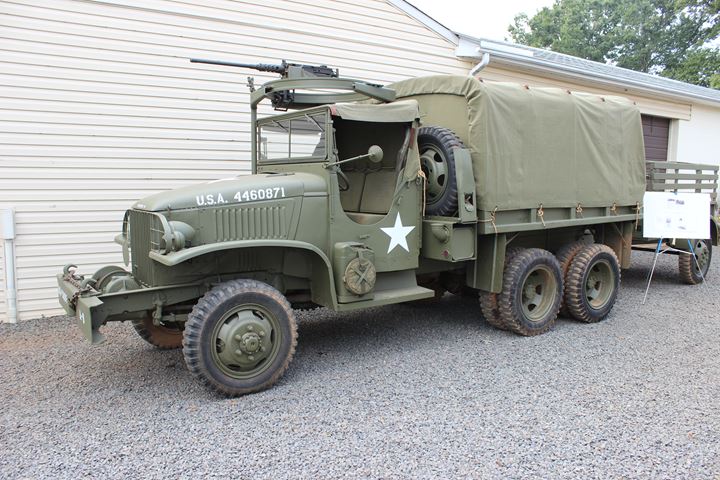

This is a post mid-1943 CCKW-352 with a winch. Author's photo.
CCKW-353:
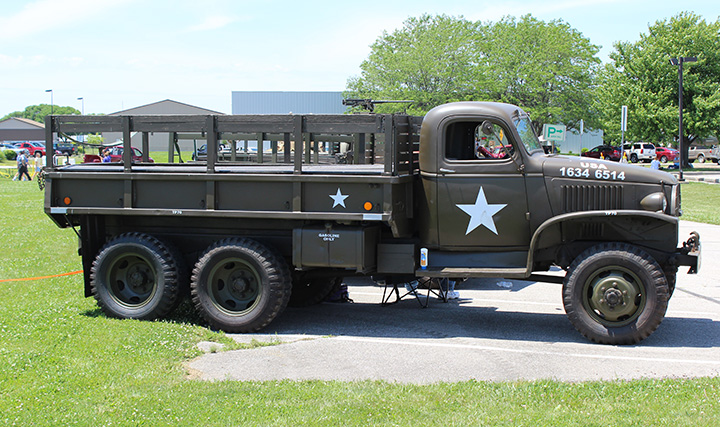

This can be identified as a CCKW-353, as
the fuel tank is underneath the bed. Also of note is that the rear
view mirrors are attached to the door hinge. After mid-1941 GMC
started mounting the rear view mirror to the cowl. Therefore, this
truck was built prior to the middle of 1941. In
this photo, the axle to the front wheel drive is visible. This is
the oldest GMC the author has found. Author's photo.

Author's photo.
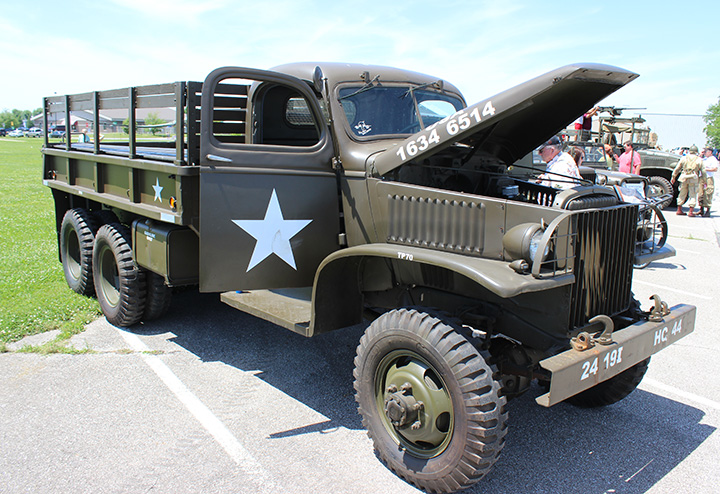
Author's photo.
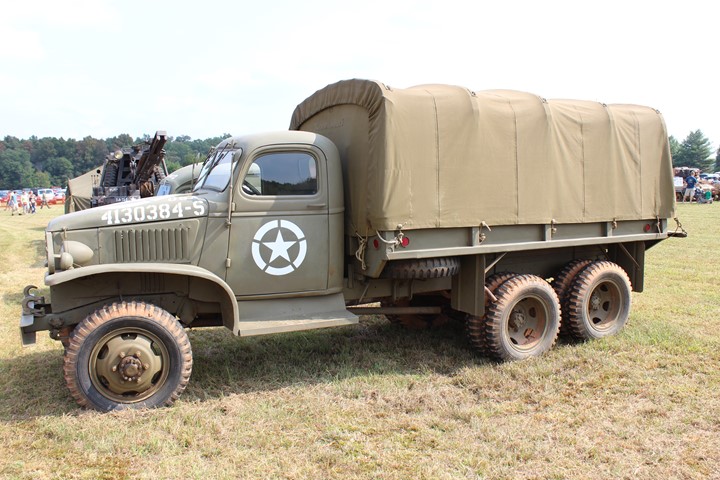

This is a post mid-1941 CCKW-353 long bed GMC truck
with no winch. It can be
identified by the spare tire and fuel tank (opposite side) that are
under the cargo bed. Because the mirror is mounted to the
cowling, this is post mid-1941. With the hardtop cab this CCKW was built
before early 1943. Author's photo.
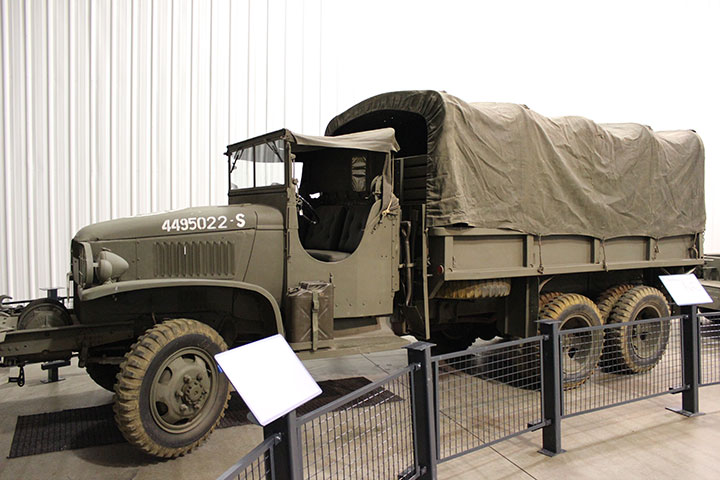

This is a post mid-1943 CCKW-353 long bed
GMC truck, as it has the soft top cab with a front winch. Author's photo.
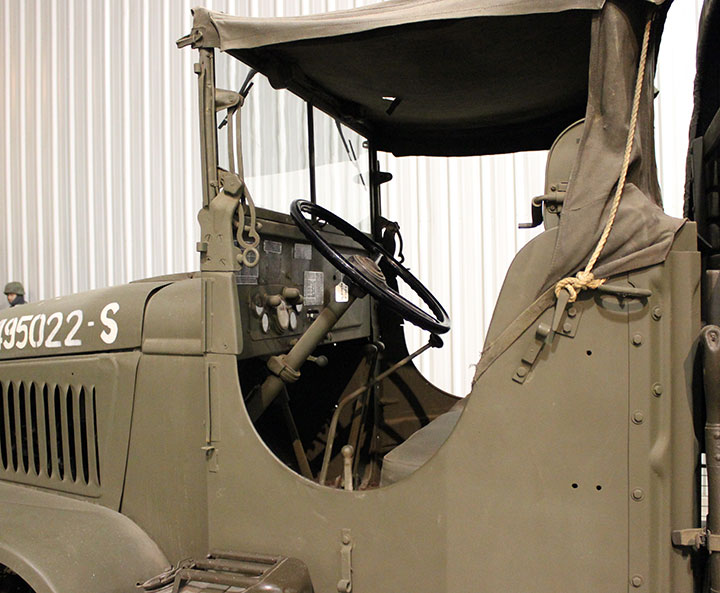

Author's photo.
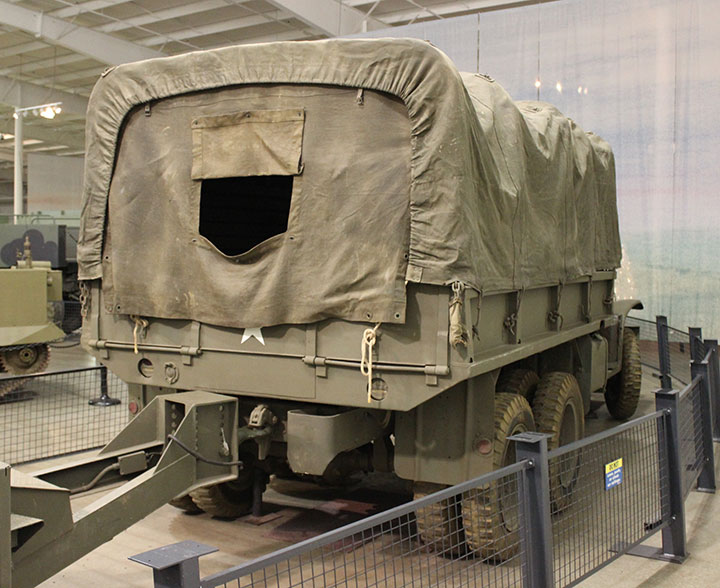

Author's photo.
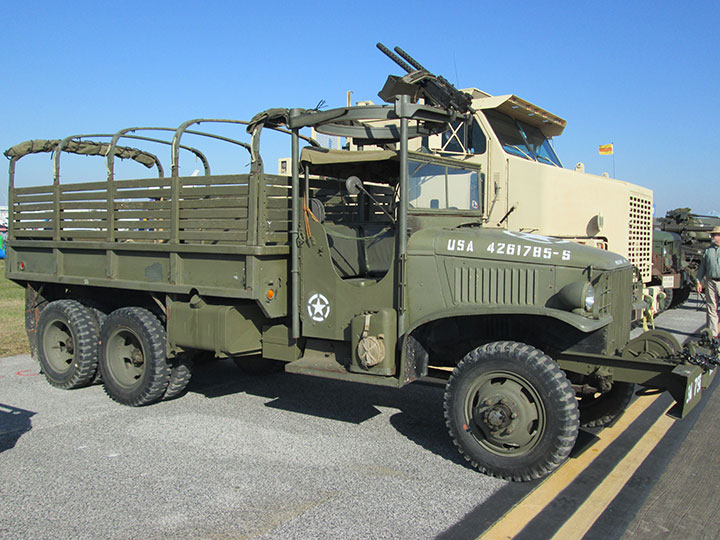

This CCKW-353 had a gun ring added for
defense against aircraft. Author's Photo.
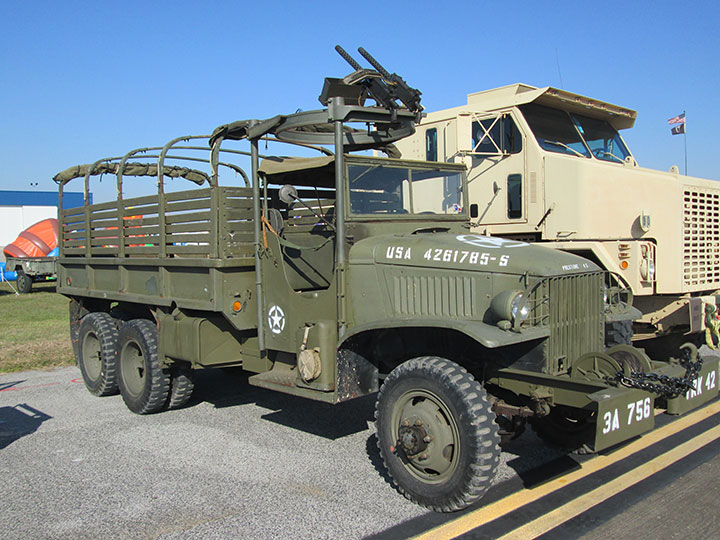

Author's Photo. Note how small it
looks compared to a modern army truck next to it.
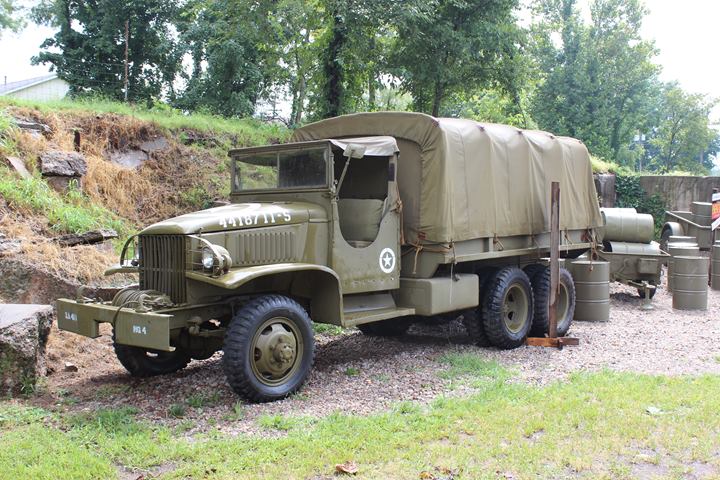

This CCKW-353 is owned by the Indiana
Military Museum in Vincennes, IN. Author's Photo.

Author's Photo.
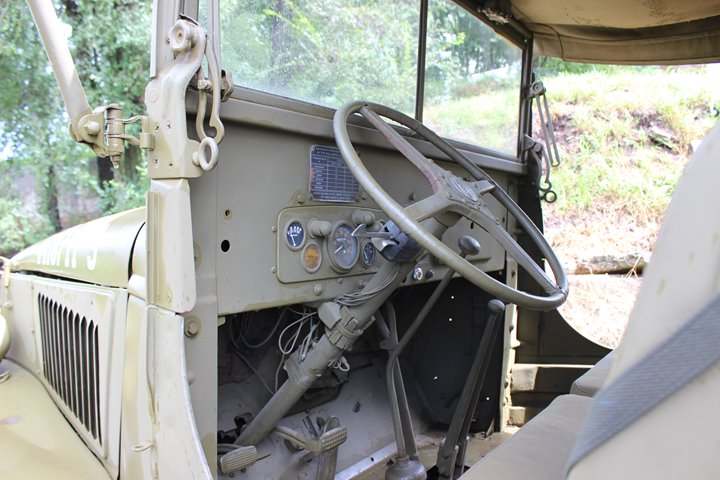

This has a four spoke steering wheel indicating it was built after
October 1943.
Author's Photo.
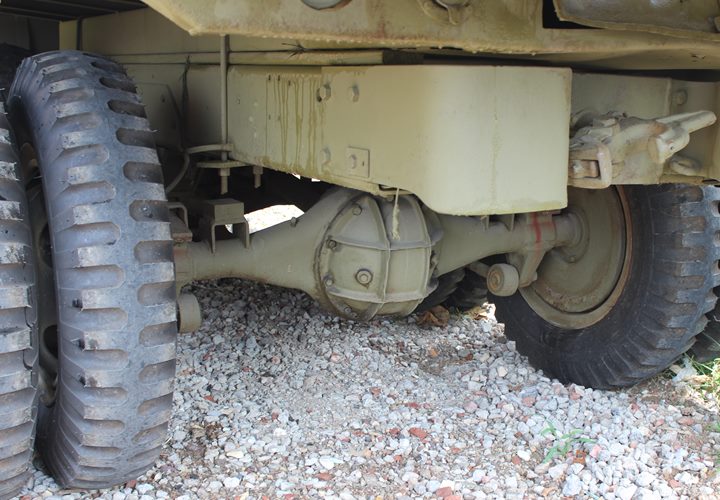

It has a Chevrolet axle. Author's Photo.
Modified or non-standard cargo bed CCKW:
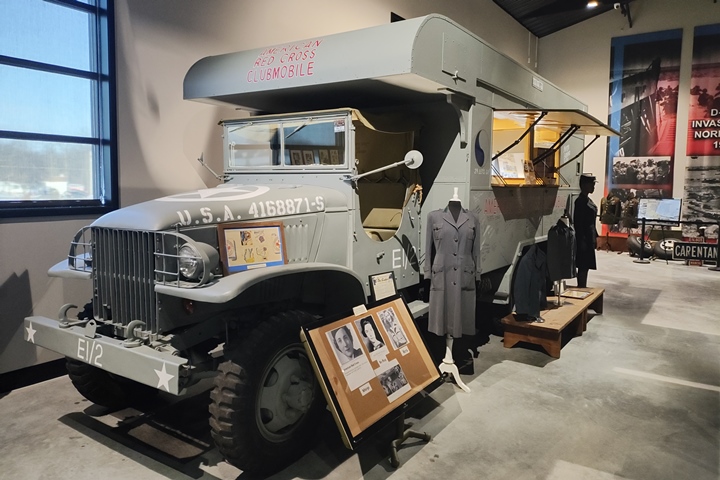

The American Red Cross operated a number of
GMC CCKW-353 as Clubmobiles. From these vehicles the Red Cross
volunteers distributed coffee and donuts to American servicemen and
servicewomen. This original Clubmobile is on display at the World
War II American Experience in Gettysburg, PA. Author's photo added
2-2-2025.
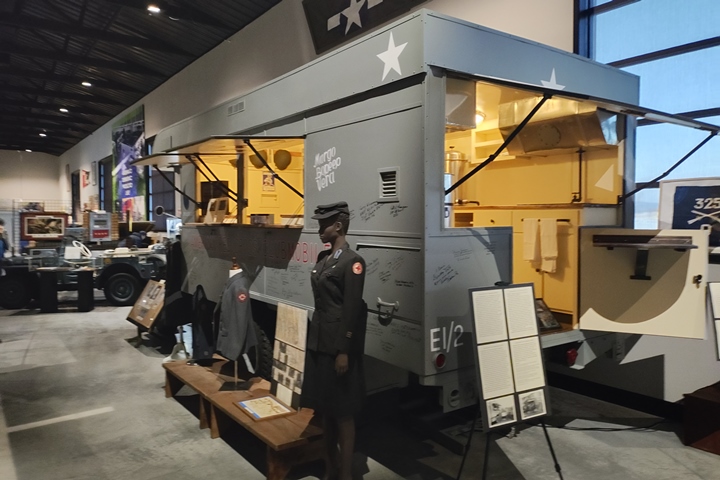

Author's photo added 2-2-2025.
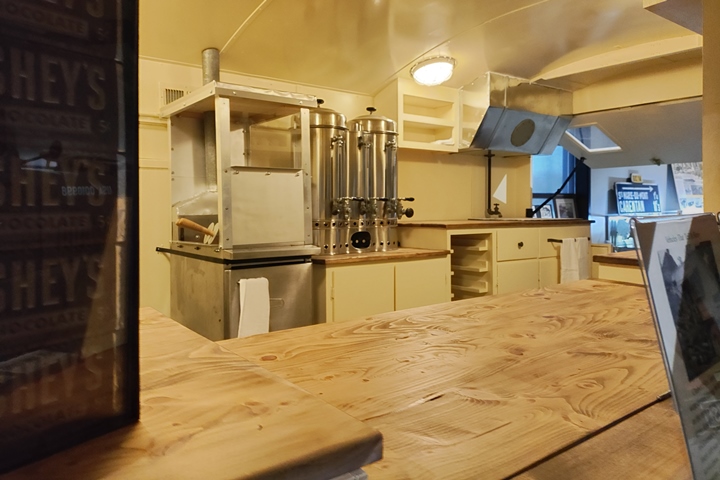

Author's photo added 2-2-2025.
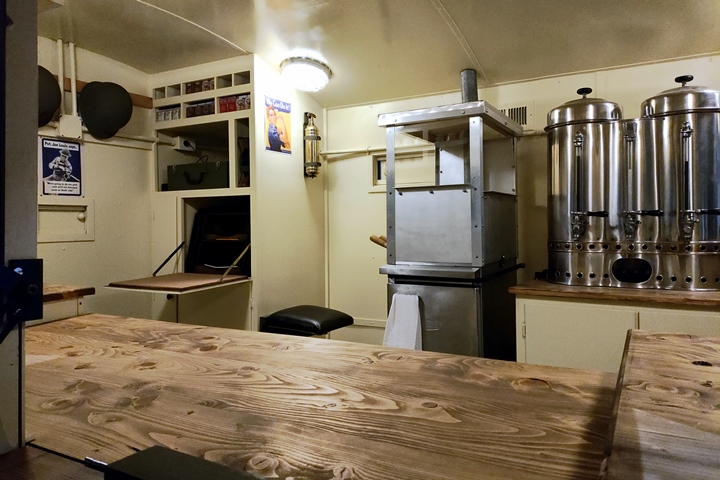

Author's photo added 2-2-2025.
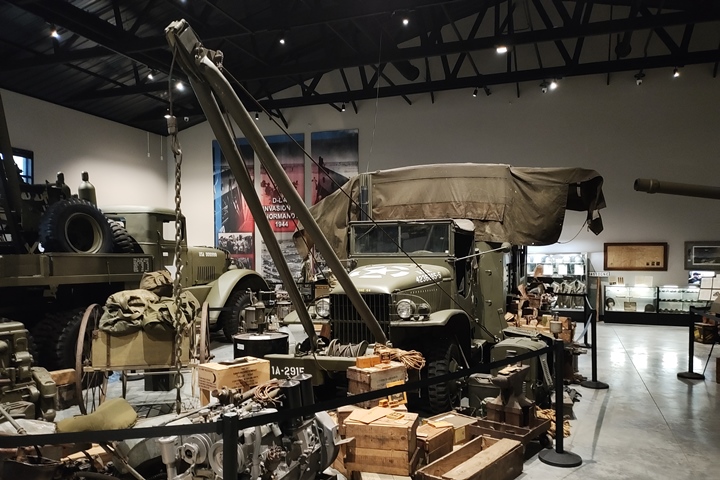

Another unique CCKW on display at the World
War II American Experience is this maintenance truck. It is part
of a larger display showing all types of equipment used in maintaining
equipment. Author's photo added 2-2-2025.
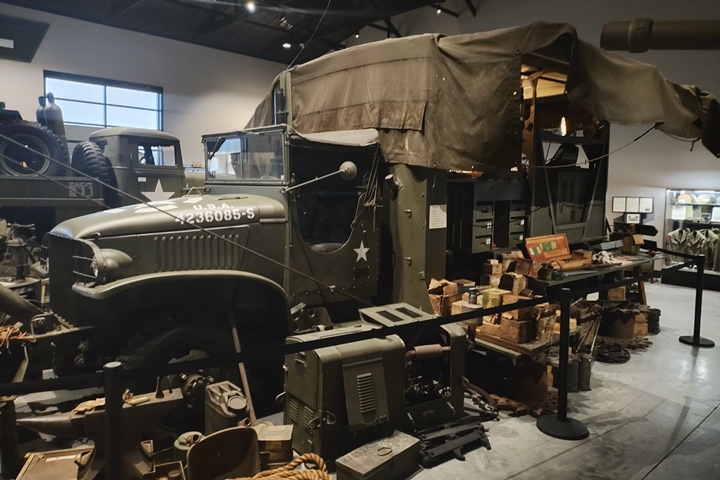

Author's photo added 2-2-2025.
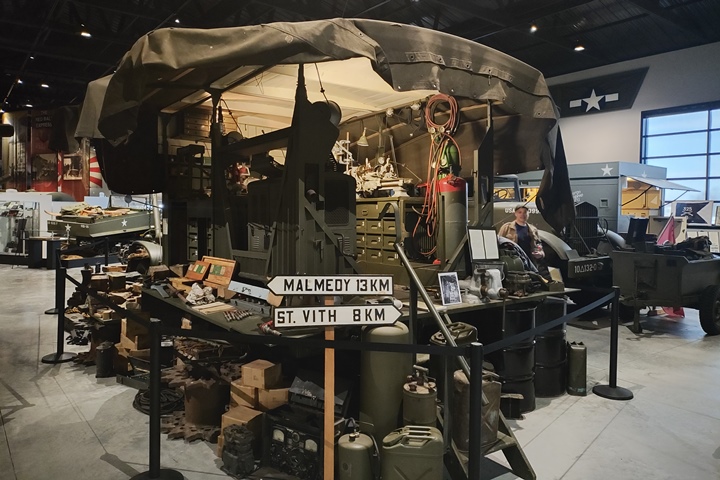

Author's photo added 2-2-2025.

Author's photo added 2-2-2025.
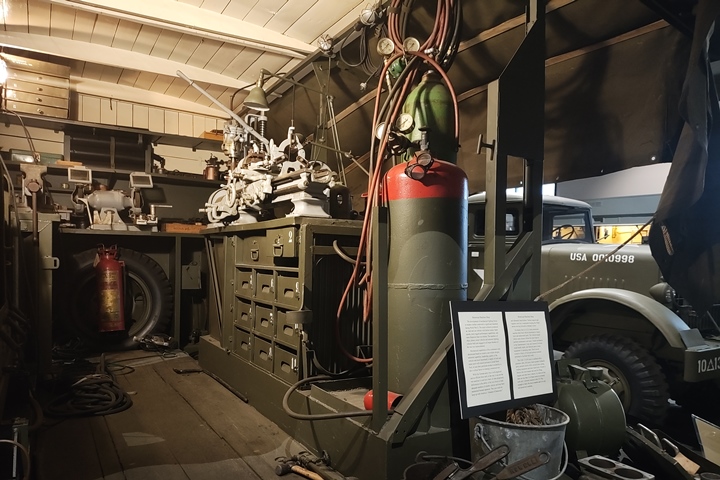
Author's photo added 2-2-2025.
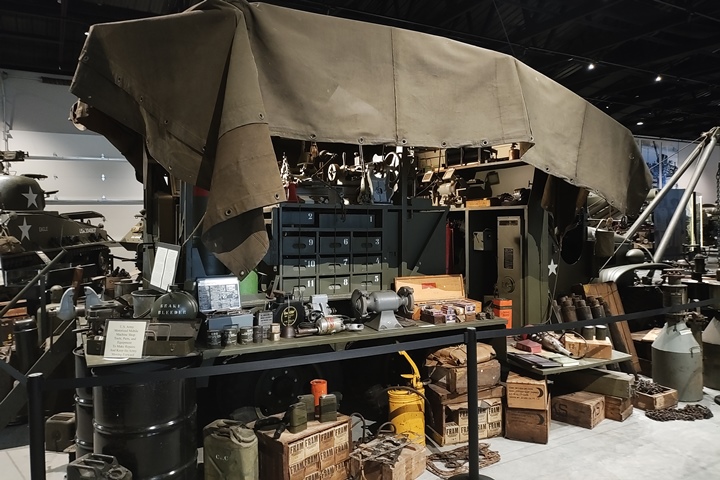

Author's photo added 1-2-2025.
There are only about a
dozen of these maintenance trucks still in existence. Two of them
are in Pennsylvania and are less than an hour's drive from each other.
The second in Pennsylvania is at the US Army Heritage Center in
Carlisle, PA as shown below.
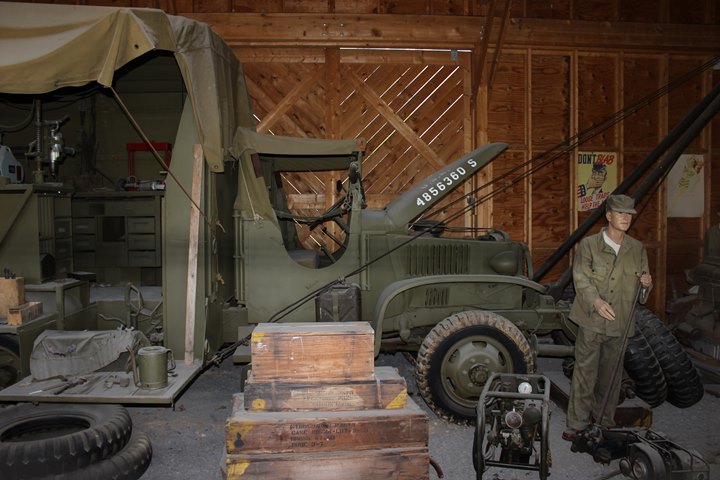

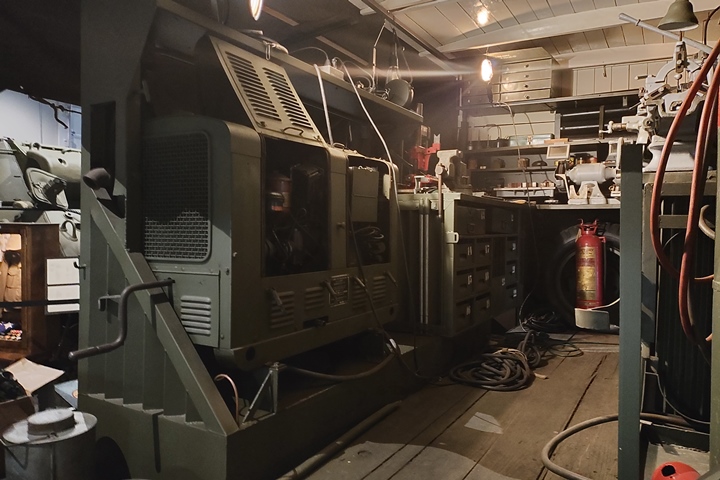
The following photos are of a CCKW-353 in a
diorama at the
US Army Heritage Center in Carlisle, PA. This particular vehicle
was configured as a mechanic's workshop truck. Author's photo.
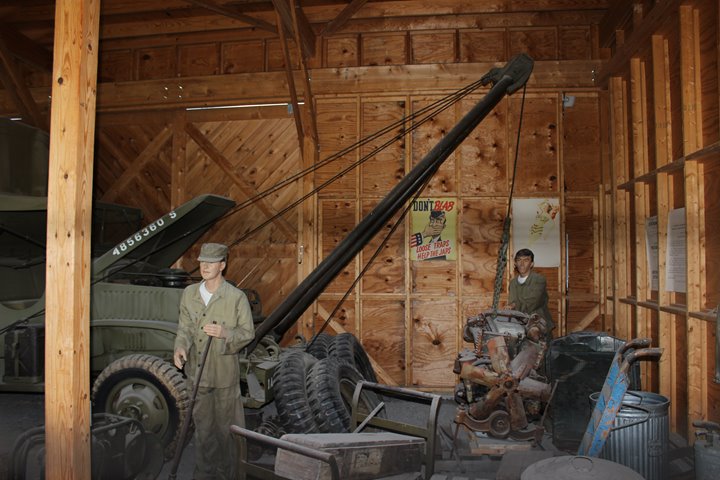

A crane has been mounted to the front of the
vehicle to pull engines that need to be replaced or rebuilt.
Author's photo.
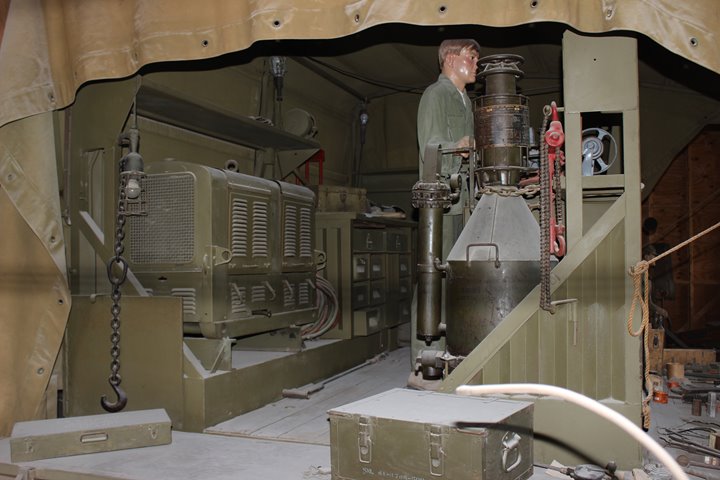

The bed of the truck has a built-in
workshop. Author's photo.
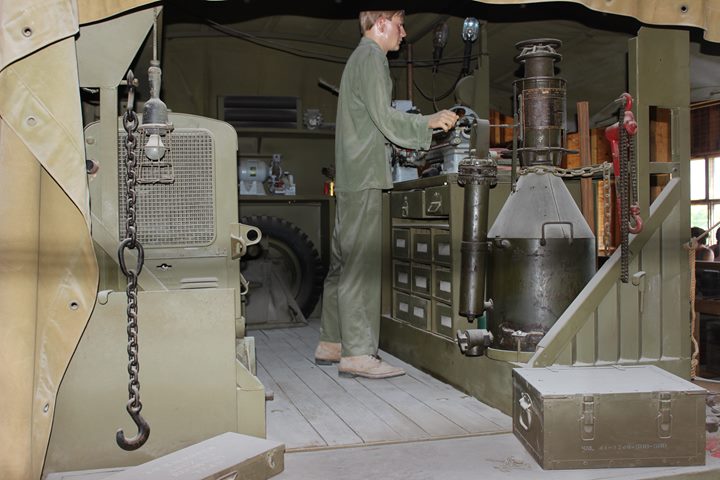

Author's photo.
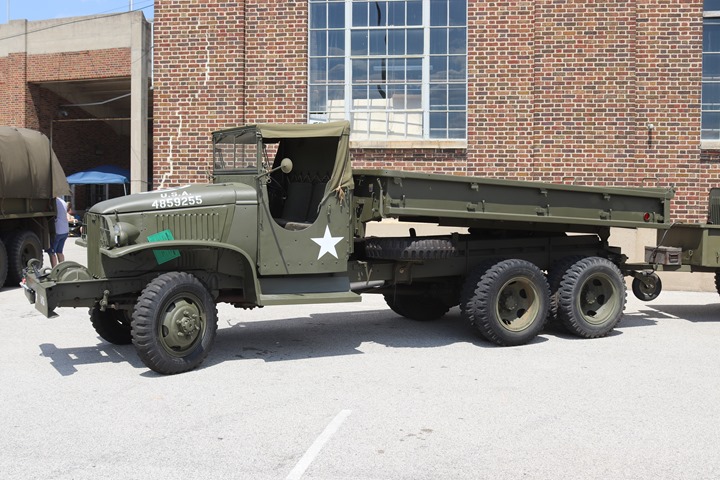

This CCKW dump truck was photographed at the
2019 MVPA Convention in York, PA. Author's Photo.
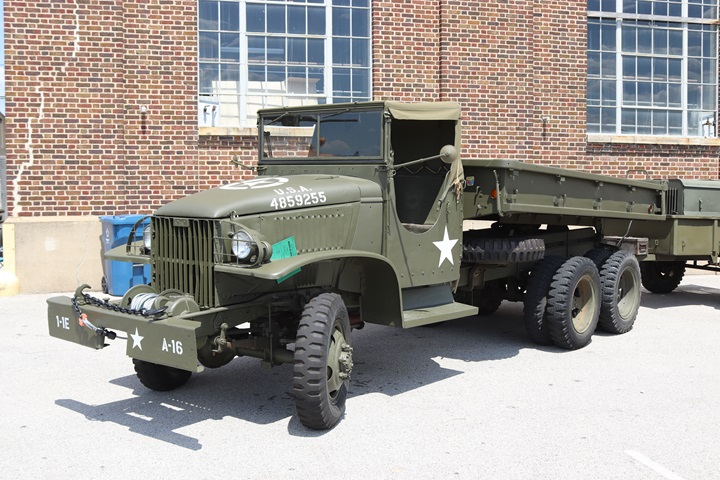

Author's Photo.

Author's Photo.

Author's Photo.

Author's Photo.
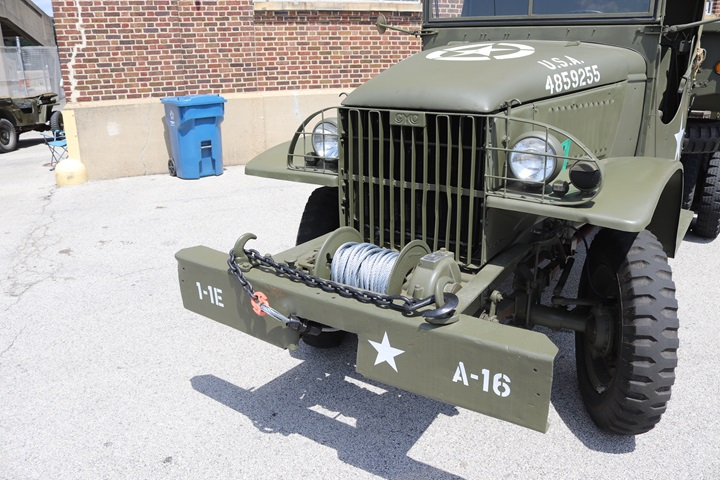

Author's Photo.

Many GMC chassis were built without the cargo bed and then sent to a
third party for addition of something other than the standard cargo bed.
This particular post mid-1941 but pre 1942 was modified as General George
S. Patton's living quarters truck. Author's photo.

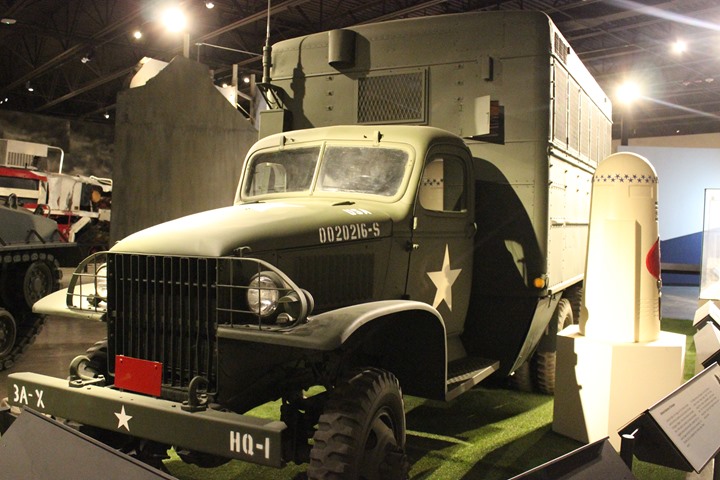
This GMC is on display at the Patton Museum at Fort Knox, KY.
Author's photo.
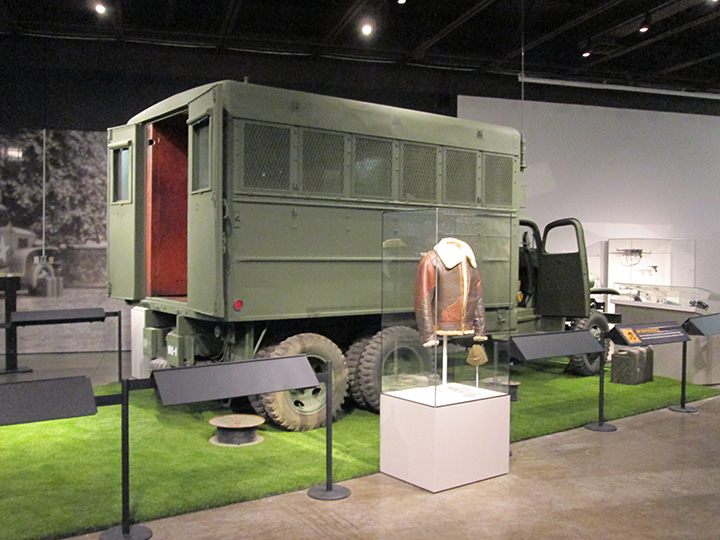

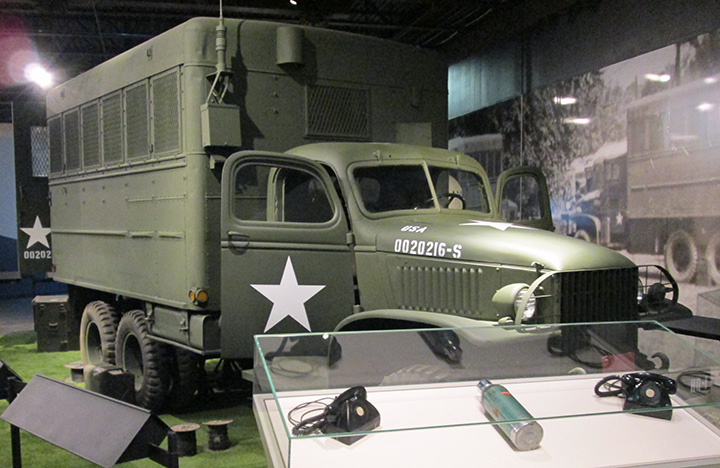
Author's photo.
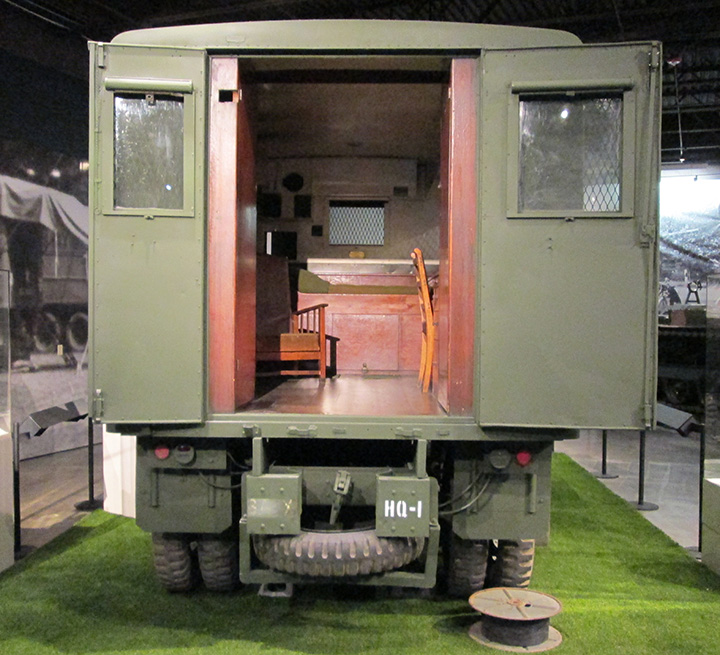

In the modification the spare tire has been moved to the rear.
Author's photo.
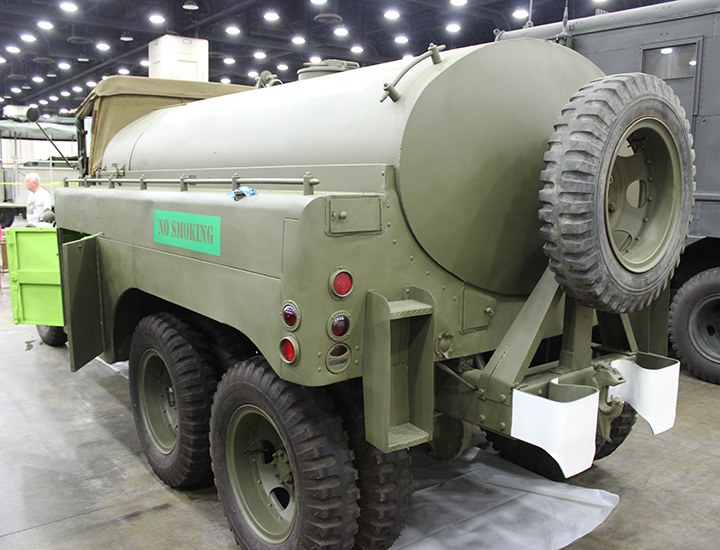
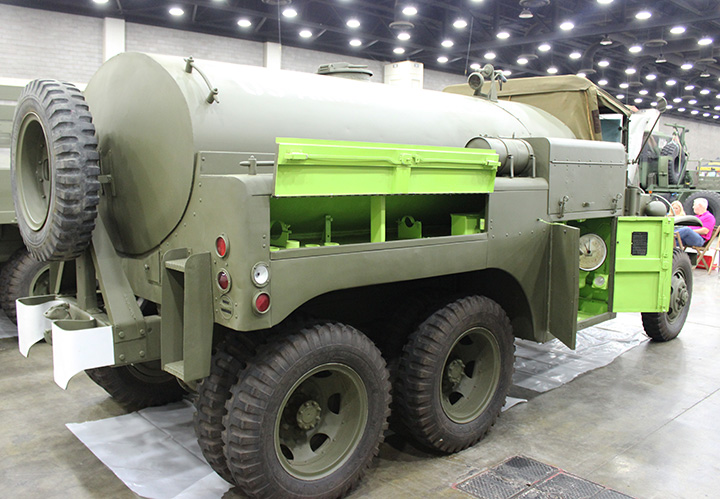
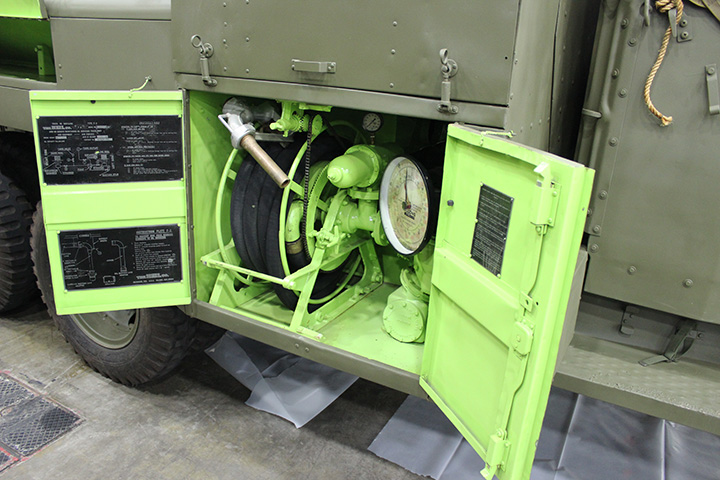
CCKW-353 Tankers:
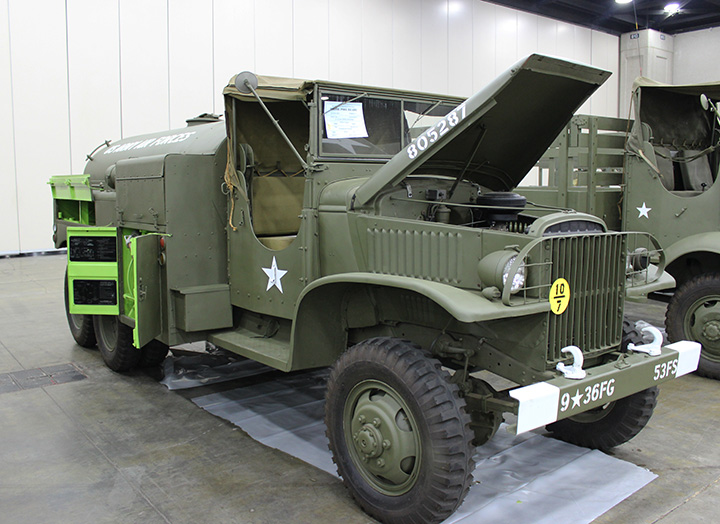

Author's Photo.
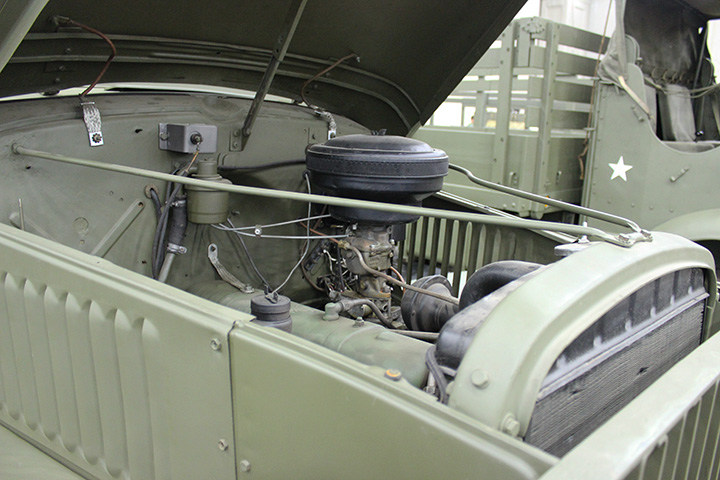

Author's Photo.
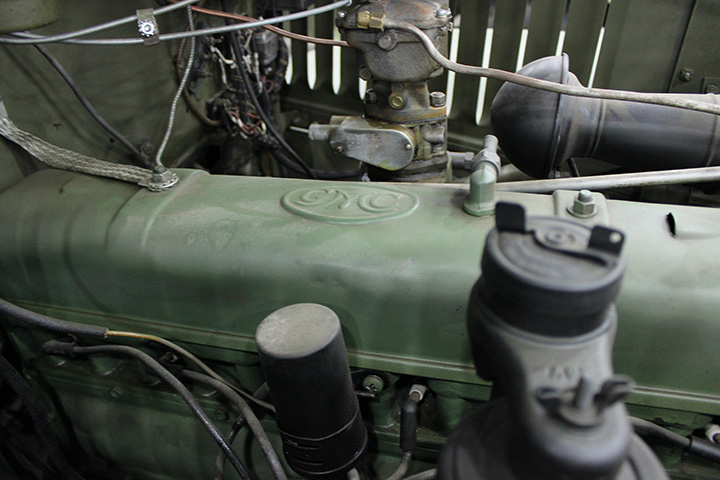

All GMC trucks were powered by the GMC 270
cubic inch engine. Author's Photo.
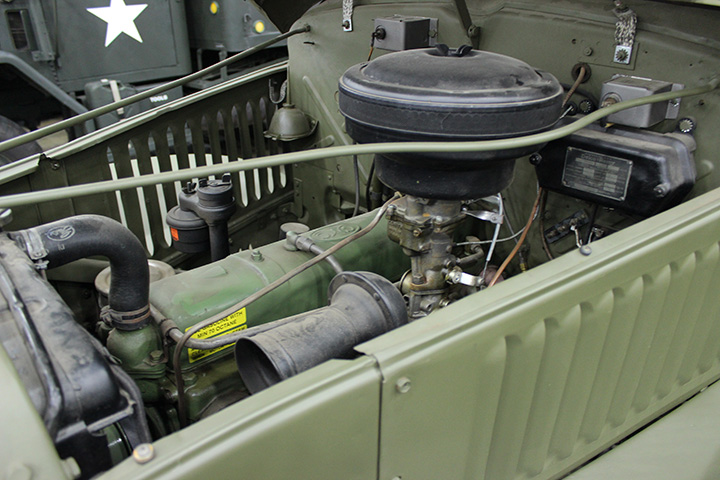
Author's Photo.

Author's Photo.

Author's Photo.

Author's Photo.
GMC CCKW with Wrecker Set #7:

Author's Photo.

Author's Photo.

Author's Photo.

Author's Photo.

GMC Cargo-Dump: A total of
37,803 cargo-dump trucks were built at both GMC Pontiac and Chevrolet
St. Louis. Some of the last of CCKW trucks built at St. Louis were
this style. All but 1,300 had winches. When production
started in April 1943, the conversion from hard cab to soft cab was also
taking place. The third open cab truck to come down the Pontiac
line was the prototype cargo-dump. Author's Photo.
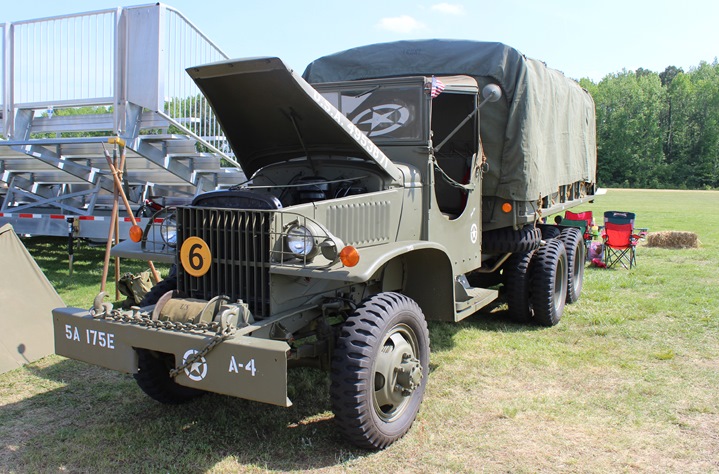

Author's Photo.
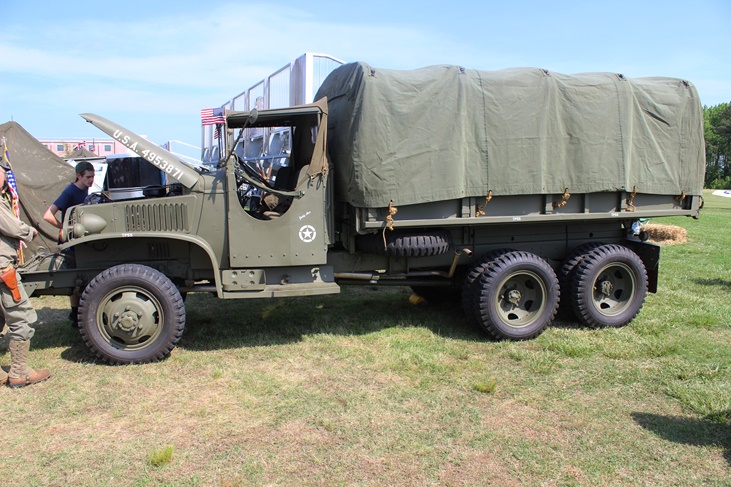

Author's Photo.
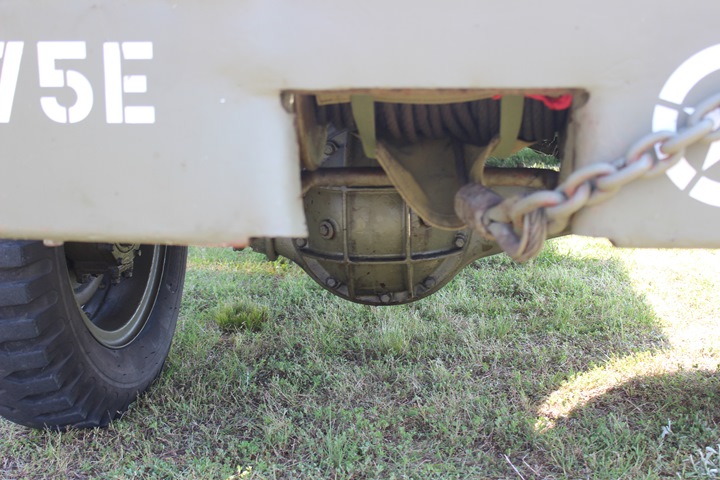

This particular truck has Chevrolet axles.
Author's Photo.

Author's Photo.

Author's Photo.
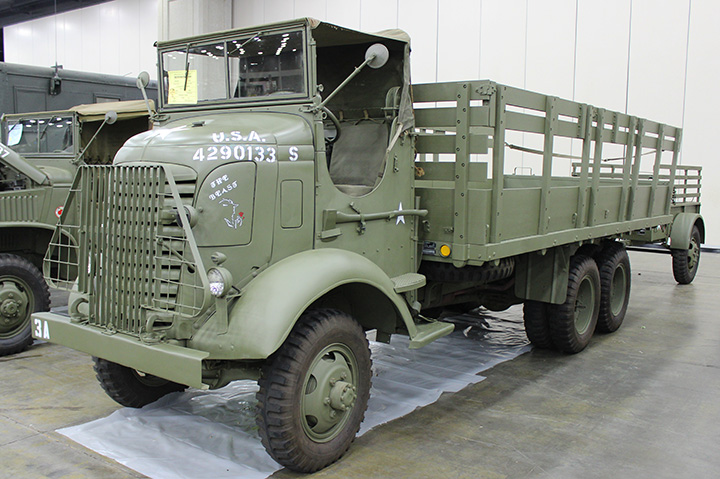
GMC Airborne Cargo-Dump:
The Airborne CCKW-353 Cargo-Dump below was one of 1,210 built by GMC at
its Pontiac plant. It is distinguishable as being built in Pontiac
because all of the airborne trucks had Timken axles and a winch.
The truck was separated into four pieces which were air transportable by
C-47 to the battlefield where they could then be assembled by the
maintenance crews.
Author's Photo.
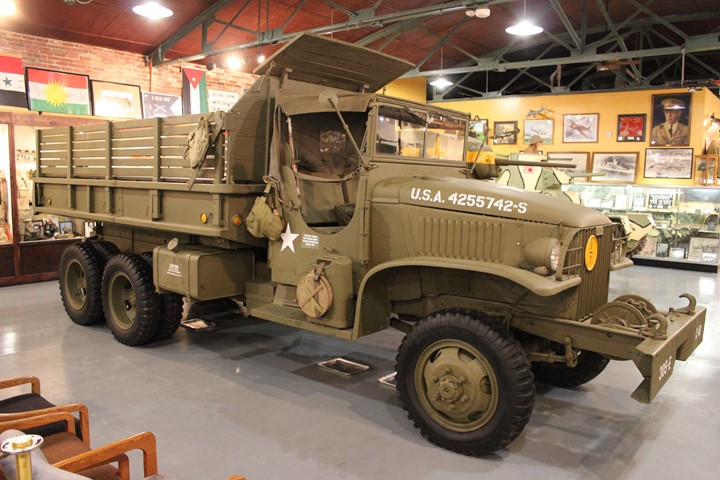

This pristine GMC CCKW-353 cargo-dump is on
display at the Indiana Military Museum in Vincennes, IN. All
airborne cargo-dumps were equipped with front winches and Timken-Detroit axles.
Author's photo.
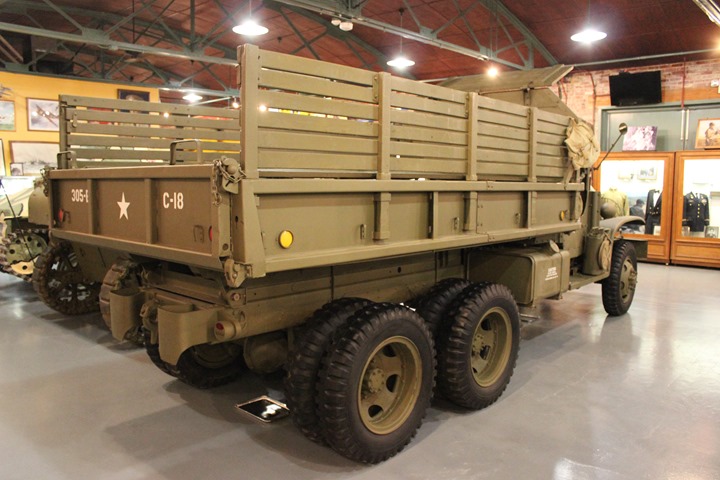

The airborne cargo-dump was only
transportable by aircraft. It could not be air dropped nor
delivered to the battlefield in a glider. Author's photo.
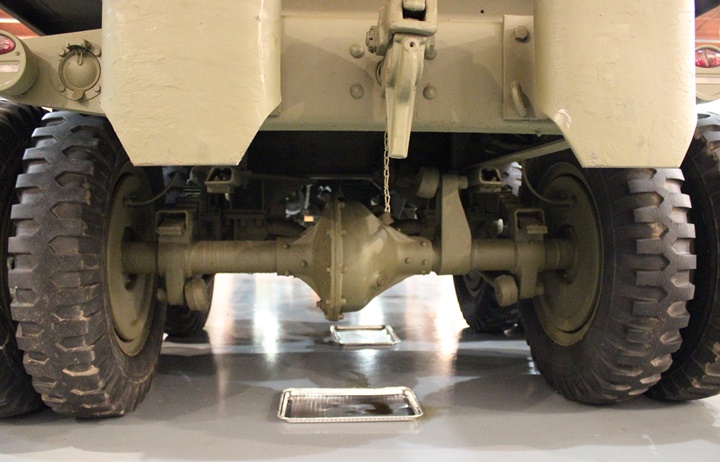

The Timken-Detroit split differential.
Author's photo.
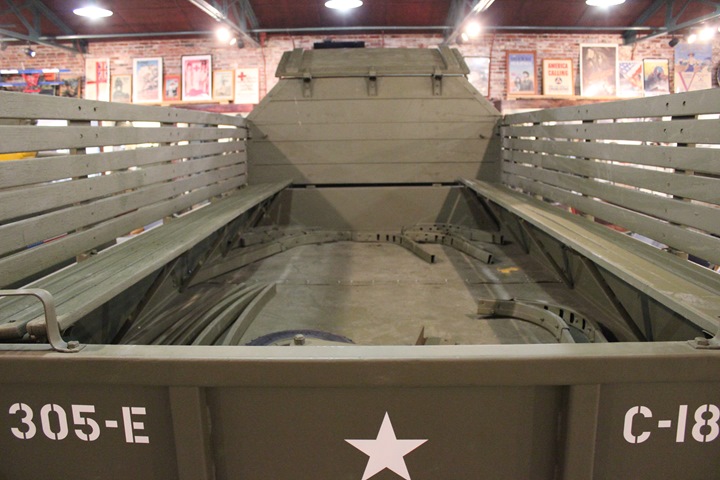

Author's photo.
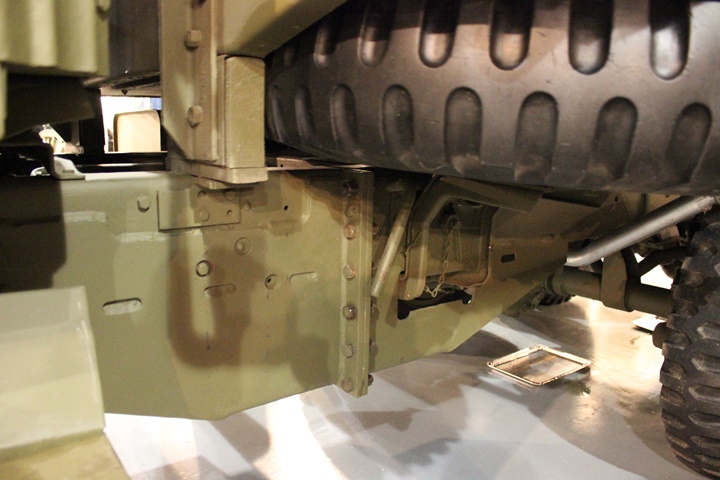

The frame was separated behind the cab with
flanges for bolting the two sections together. A special valve and
coupling were provided to keep from introducing air into the brake lines
upon re-assembly. The two drive shafts were disconnected at the
transfer case. Author's photo.
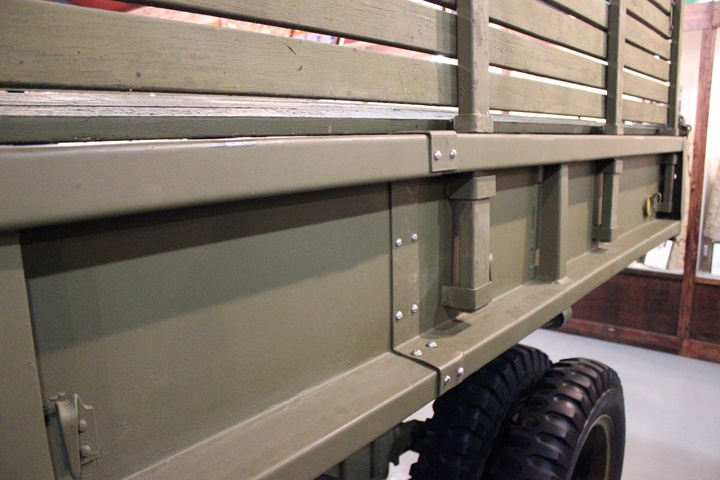

The cargo bed also came in two pieces and
bolted together. In theory a team of five experienced mechanics
could assemble the truck two hours after it was unloaded from the two
C-47s needed to transport it. The front section with the cab came
on one C-47 and had the front half of the bed, running board, fenders,
bows, tarpaulin windshield and tools were loaded in the front cab.
The front section came with a dolly attached to the rear for ease of
movement before being assembled. The second C-47 would arrive with
the rear half of the chassis. The rear half of the bed, spare tires,
fuel tank, muffler, body racks and frame splicing were loaded in the
aircraft behind the rear frame. It took less than an hour to
unload both sections from their aircraft. Author's photo.
The AFKWX: A = 1939 design, F = Forward cab,
K = All wheel drive,
W = Tandem rear wheels, X = Extended bed
GMC built 7,232
of the AFKWX which was a cab over engine design with a longer cargo bed
for transporting bulky loads. It had the same wheelbase as the
CCKW-353 and had a 15 or 17 foot bed which was three or five feet longer than the 353
series truck. Being of an older design it did not have a tilt cab
which made working on the engine a challenge. The GMC 270 engine
had an updraft carburetor rather than a downdraft as was on the CCKW 270
engine.

Author's Photo.
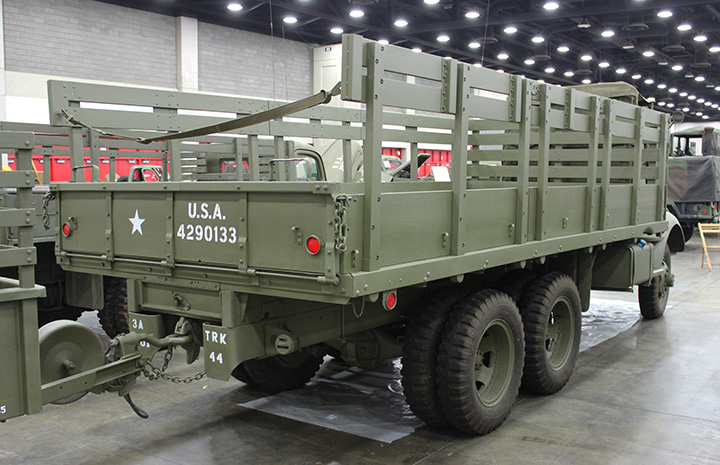

The cargo bed is fifteen feet long and was
designed to carry bulky loads. Author's Photo.
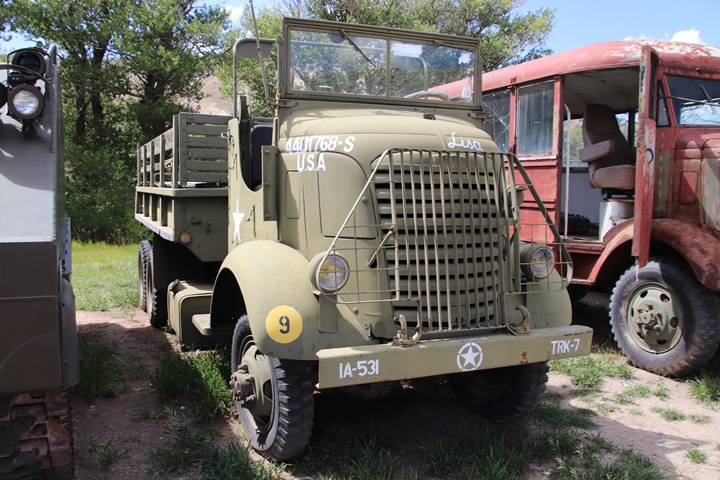

This example of a GMC AFKWX-353 is on
outside display at the National Museum of Military Vehicles in Dubois,
WY. Author's photo added 2-2-2025.

There is not much left of the data plate but
it does show that this is a AFKWX-353 and is apparently serial number
9501. Author's photo added 2-2-2025.
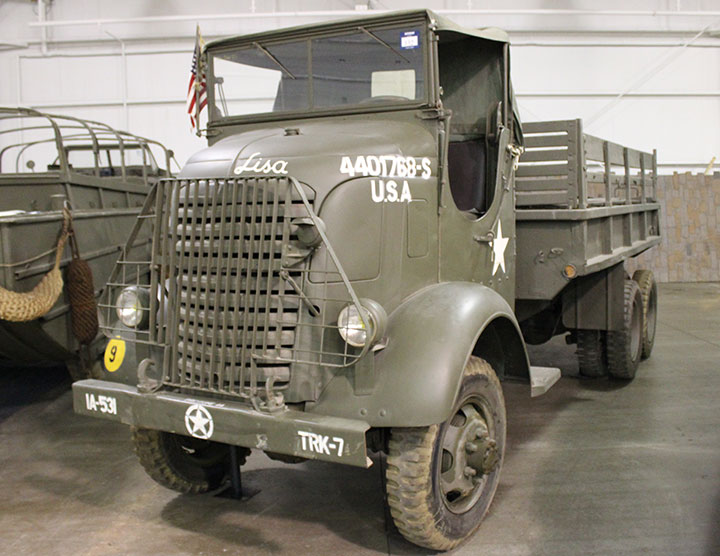

I first saw this truck in 2014 at the now
closed National Military History Center in Auburn, IN. This museum
closed in 2021 after gradually selling off its vehicles and artifacts.
Author's photo added 2-2-2025.

Author's photo added 2-2-2025.
AFKX-352 4x4 GMT 1.5-Ton
Machine Shop: During 1940-1942 GMC built 1,943 AFKX-352 Cab over
Engine 4x4 vans for use by the U.S. Army as maintenance vehicles.
I have found three of these trucks to date. The first example shown
below which is located at the Liberty Aviation Museum in Port Clinton, OH was used by the
Army Ordnance Department for the repair of weapons in the field.
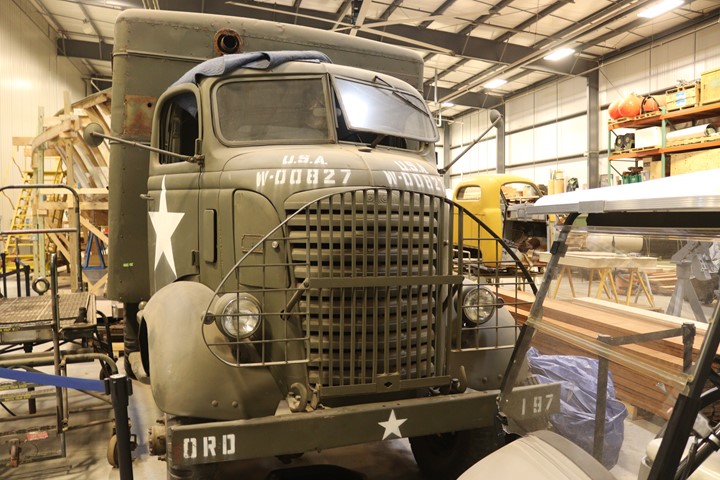

Note that the front end is similar to the
AFKWX in the photos above, except that this has the older steel roof,
rather than the later soft canvas cab. Author's photo added 4-21-2019.

Author's photo added 4-21-2019.
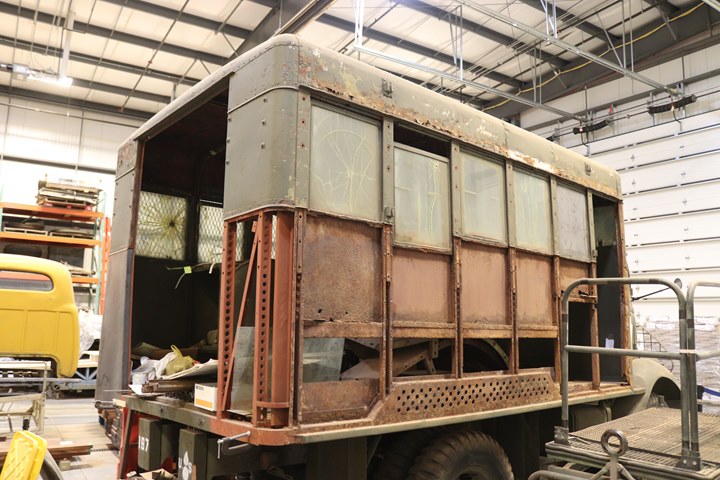

The AFKX-352 4x4 is located in the boathouse section of the museum, where Vosper PT boat 728 is being restored.
The truck is located there waiting to be restored. However, one of
the advantages of not being restored is that the construction of the
machine shop is evident. On this side the glass windows at the top
can be slid down the tracks for ventilation. Author's photo added
4-21-2019.
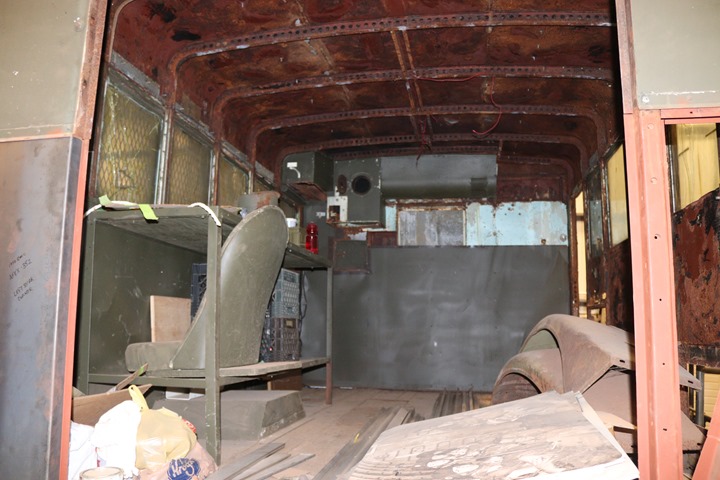

All of the equipment is gone out of the
inside, and it is being used for storage. Author's photo added
4-21-2019.
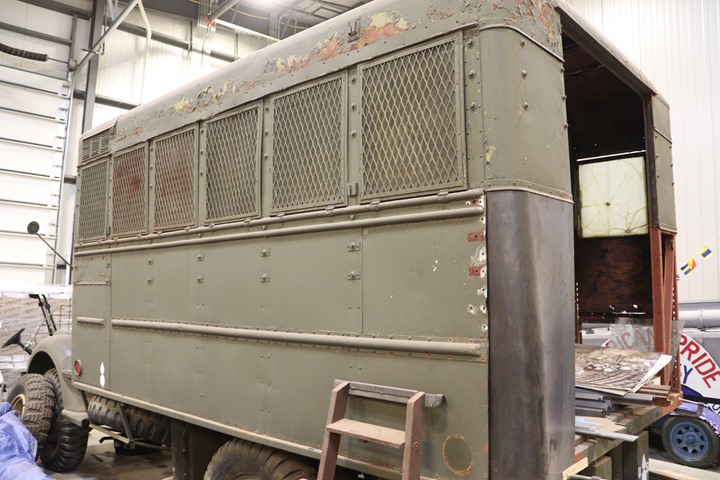

On this side the windows are covered by
expanded metal coverings, which pivot on hinges below the windows.
Author's photo added 4-21-2019.
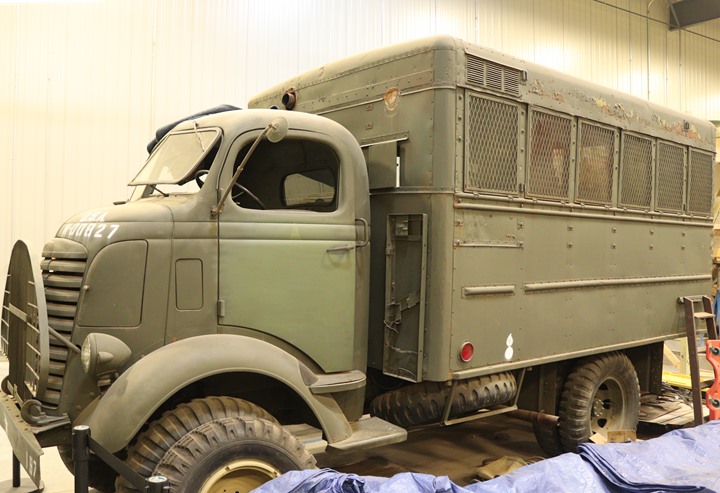

W-00827 was built in 1940 as one of 276
built under GMC contract number 7413. Author's photo added 4-21-2019.
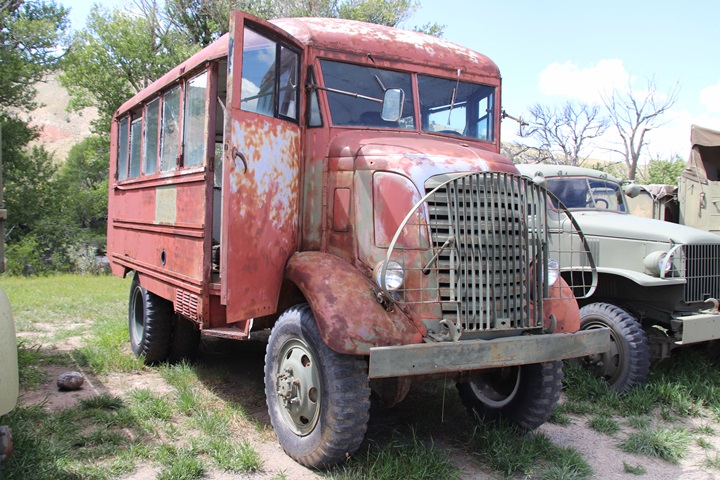

This example of a GMC AFKX-352 is awaiting
restoration at the National Museum of Military Vehicles in Dubois, WY.
Author's photo added 2-2-2025.
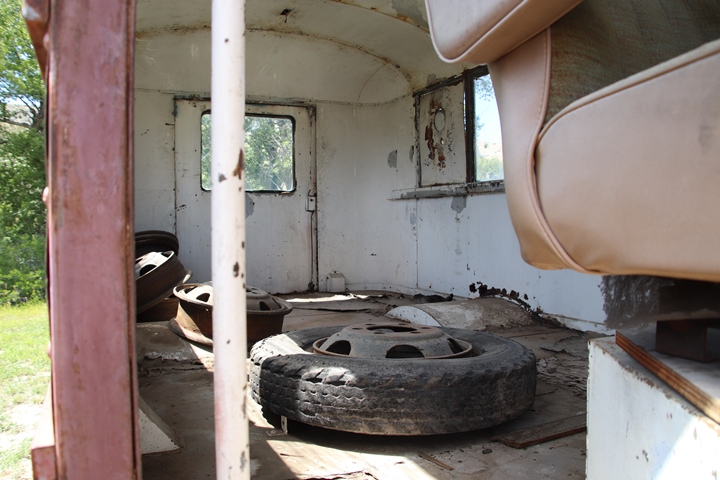

Author's photo added 2-2-2025.

The data plate shows this vehicle was
delivered on 8-26-41 and is serial number 1904. Author's photo
added 2-2-2025.

The Wheels of Liberation in Gettysburg, PA
has in its collection a GMC AFKX-352 that was a spare parts truck.
Author's photo added 2-8-2025.

Author's photo added 2-8-2025.

Author's photo added 2-8-2025.

This vehicle was delivered on 5-16-1942 with
serial number 2718. Author's photo added 2-8-2025.
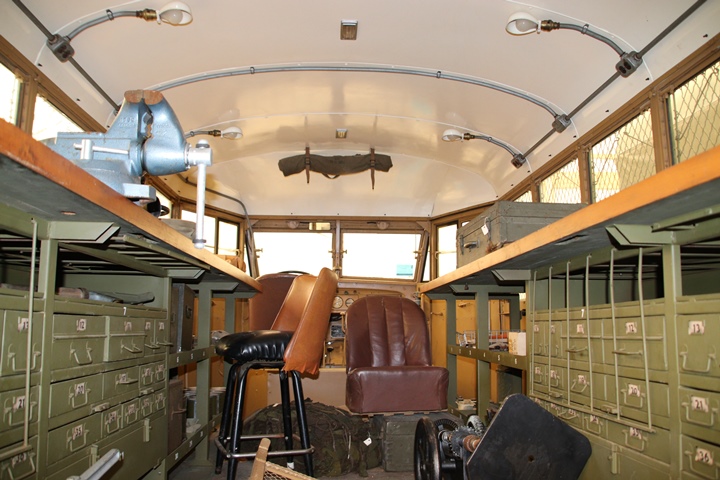

Author's photo added 2-8-2025.

Author's photo added 2-8-2025.
GMC Switch Engines:

This CCKW was used in
England as a switch engine working inside of a warehouse to avoid fire
hazard.
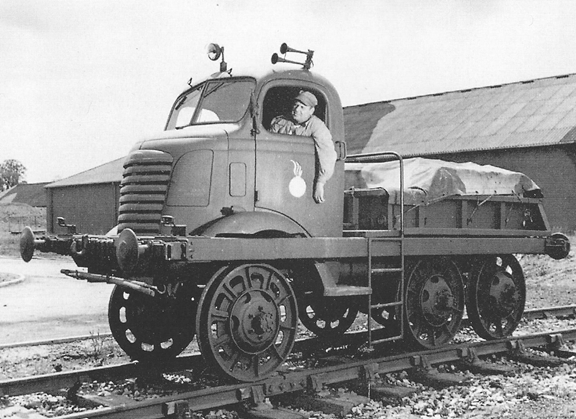

This AFKWX was used as a switch engine
in Ashchurch, England during the war.
DUKW: D = 1942 design, U =
Utility (Amphibious),
K = All wheel drive,
W = Tandem rear wheels
The first use of the GMC DUKW amphibious truck was the invasion of
Sicily in July and August 1943.
A quote from "The Great Crusade" by General
Dwight D. Eisenhower in reference to the Sicily invasion: "This
change resulted from the unforeseen availability of a considerable
number of LST's and the quantity production of the "duck", an amphibious
vehicle that proved to be one of the most valuable pieces of equipment
produced by the United States during the war."
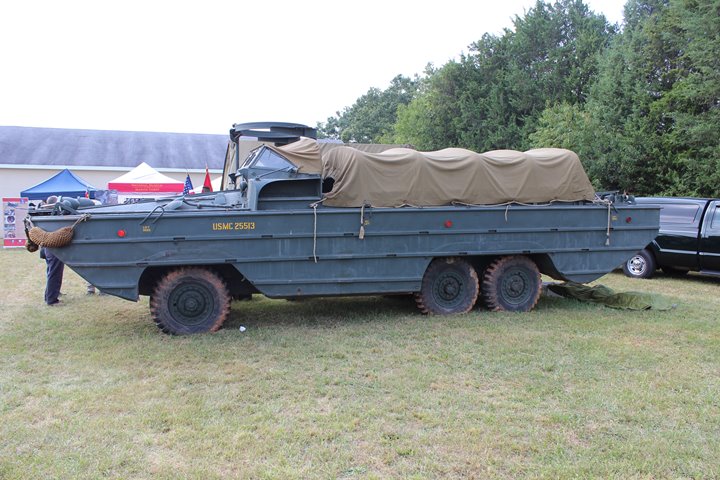

Author's Photo.
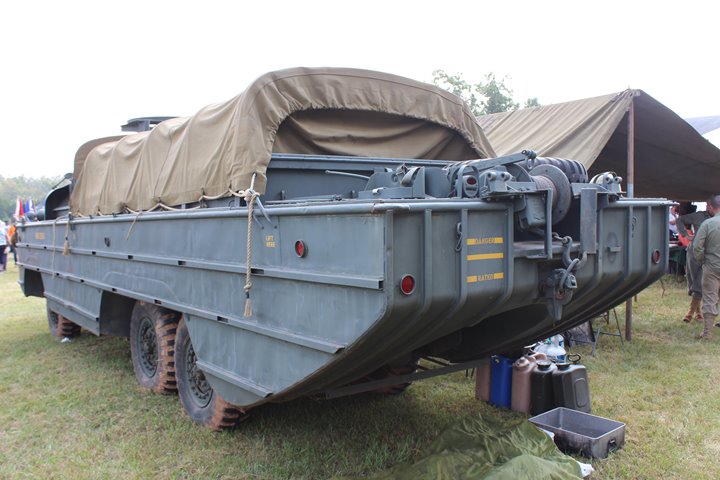

Author's Photo.
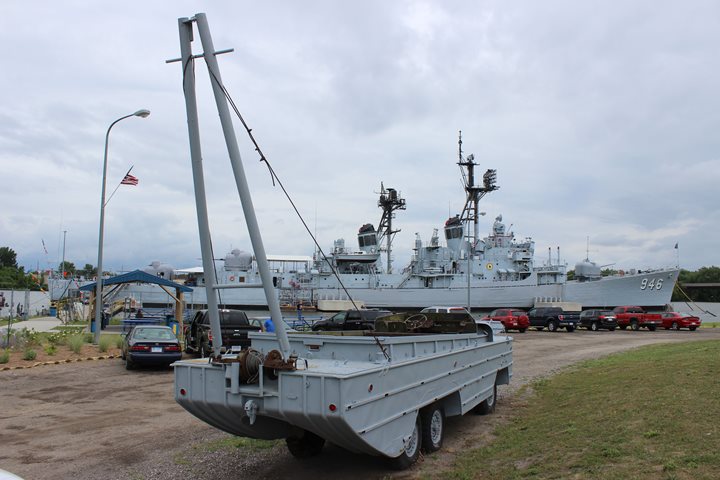

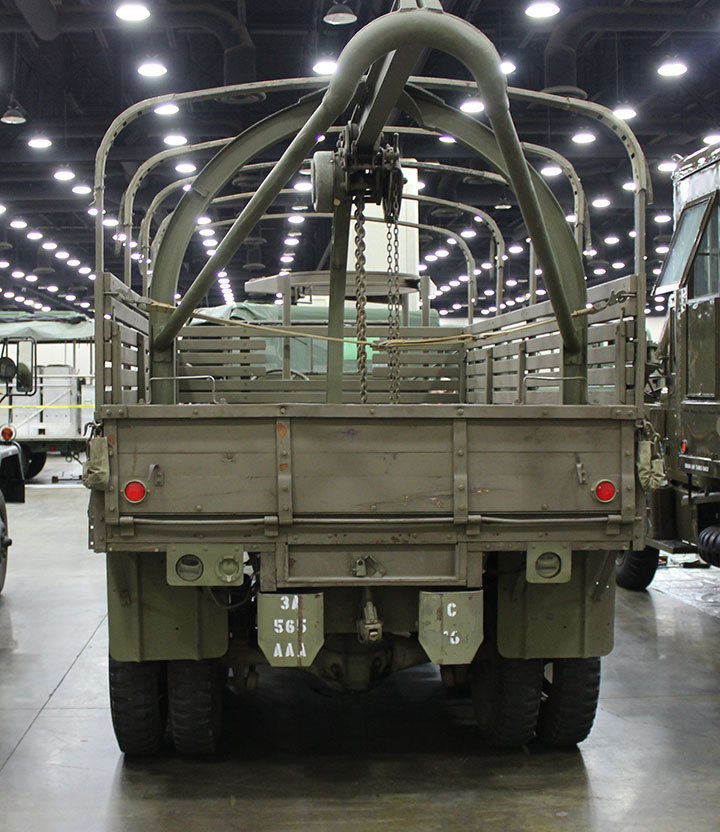
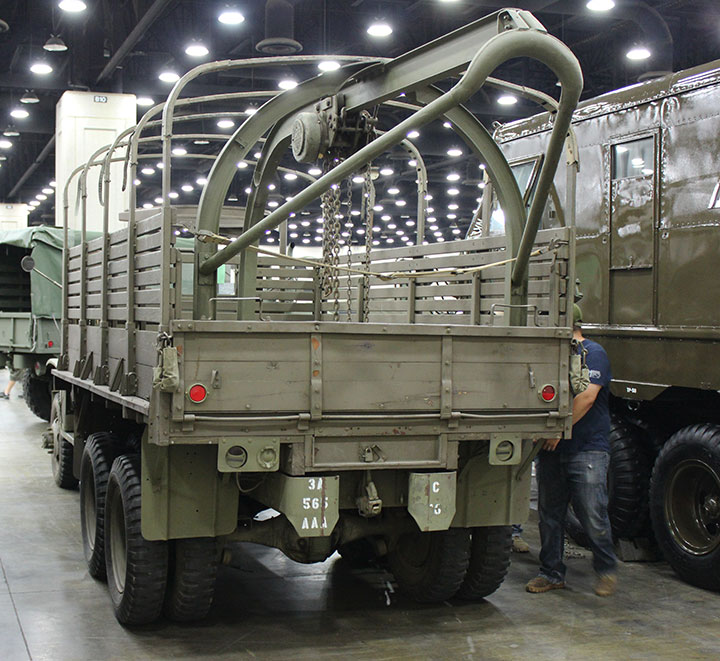
This GMC DUKW is on display at the USS Edson
in Bay City, MI. One in four DUKWs were built with the crane to
facilitate unloading other DUKWs during World War Two. Assuming this vehicle
was built in Pontiac, it is only 95 miles from where it was assembled. Author's Photo.
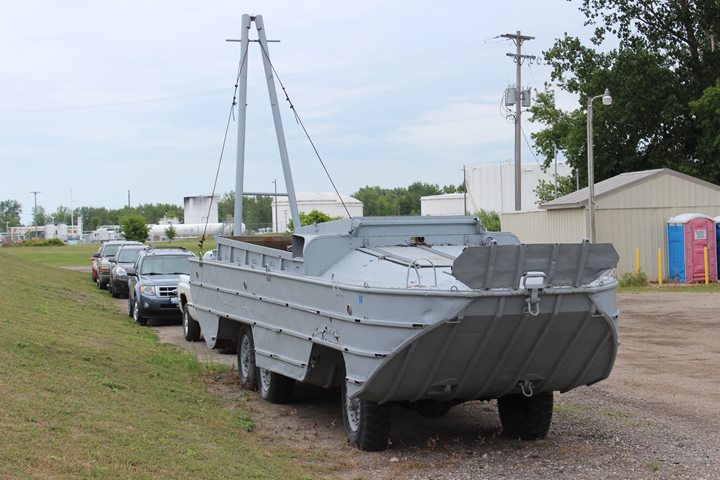

Author's Photo.
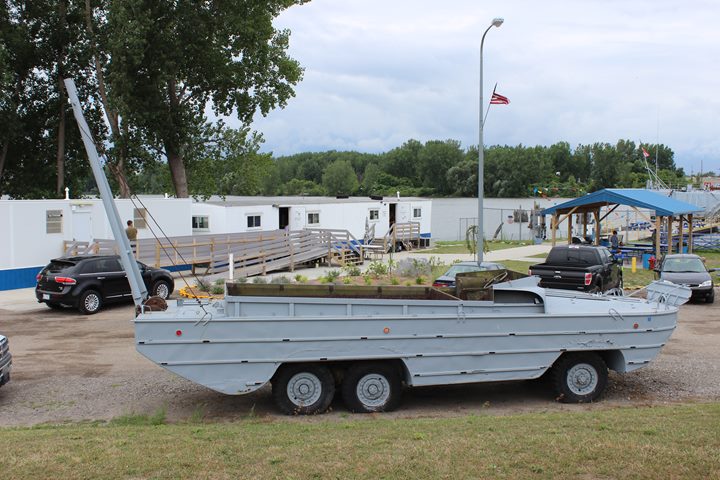

Author's Photo.
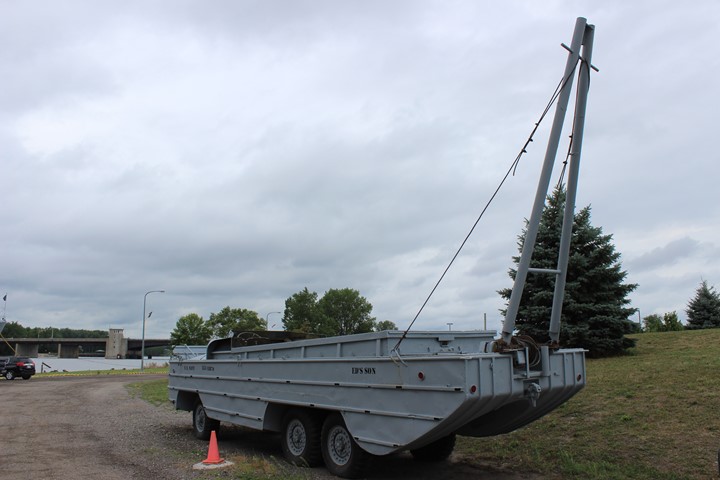

Author's Photo.
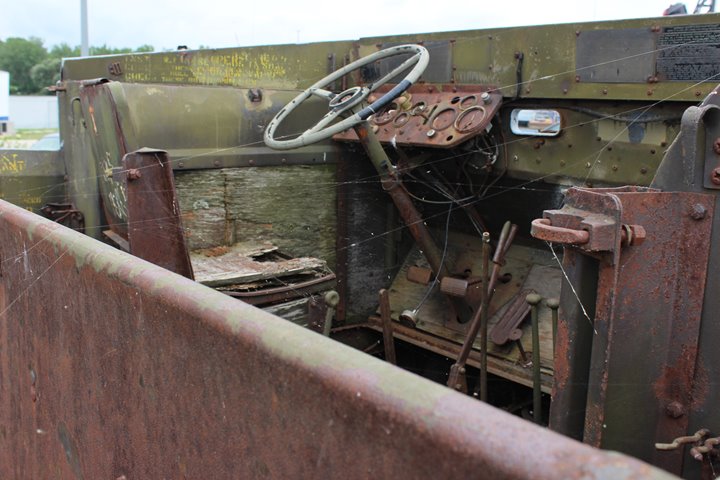

Author's Photo.
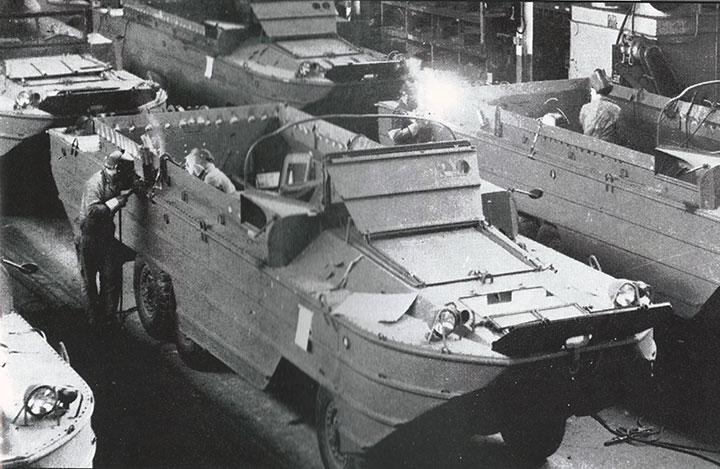
DUKWs under construction at the GMC Pontiac
plant.
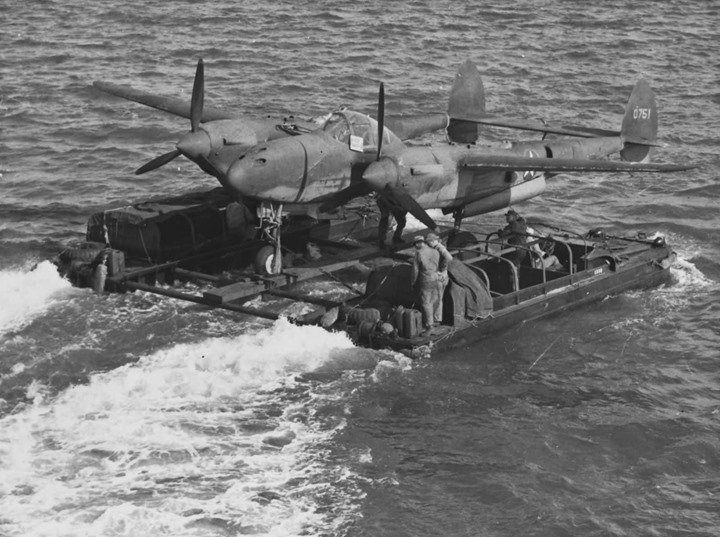

The GMC DUKW was versatile. Here two of them joined together move
a Lockheed P-38 across a body of water.
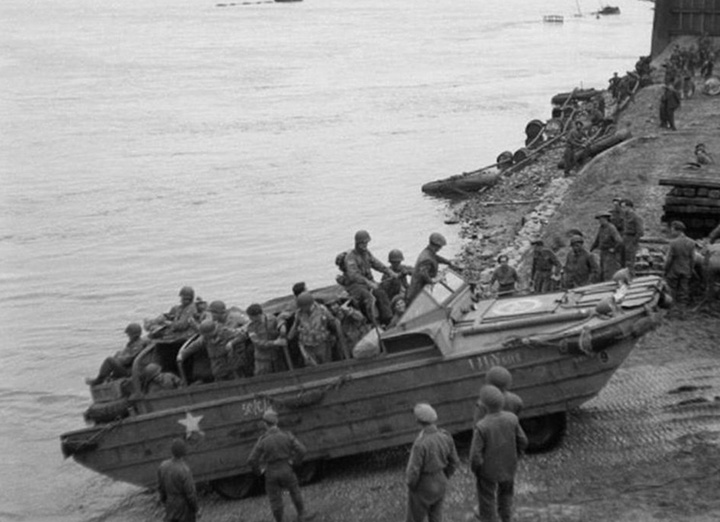

Not only was the DUKW used from ship to shore on ocean beaches, but it
moved inland in Europe to bring supplies and troops across the many
rivers that need be crossed.
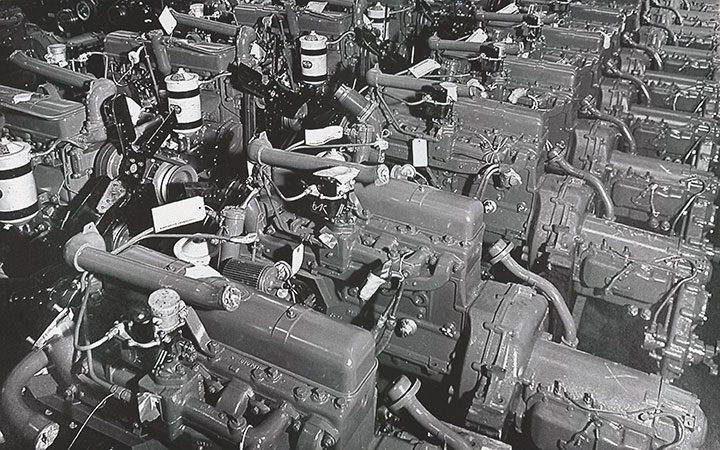
GMC 6
cylinder 125 hp engines that went into all of the GMC 2-1/2 ton trucks
are shown in this factory photo of the era.
The engine was also used in the Chevrolet-built T17E1 Staghound armored
car and the GMC-built T18E2 Boarhound armored car.
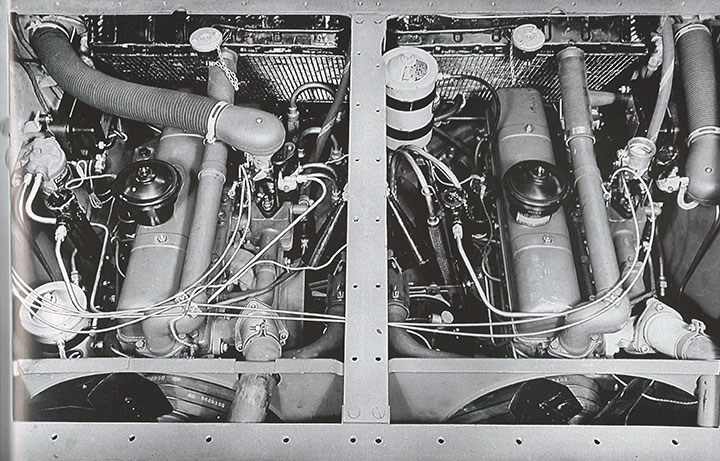
Both the Staghound and Boarhound used two of the GMC engines to power
the armored cars.

GMC built 30 T18E2 Boarhound armored cars for the British. The
original order was for 2,500 but that did not transpire.

Eight GMC-built Boarhounds ended up in combat with the British in North
Africa. Today only one Boarhound still exists at the Tank Museum
in Bovington, UK.
The GMC Rear Wheel Drive System:
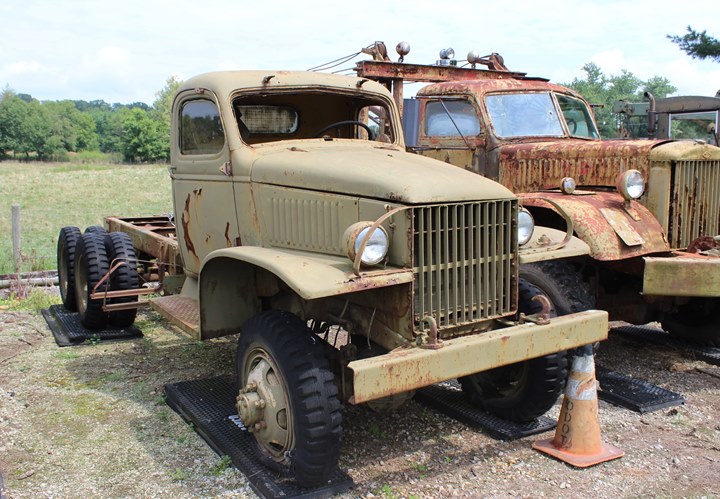

This derelict CCKW-353 at the Fort Economy
Museum in Hallsville, OH allows one to look at the drive train for GMC
trucks built during World War Two. With the mirror mounted to the door, this
vehicle was built before mid-1941. Author's Photo.
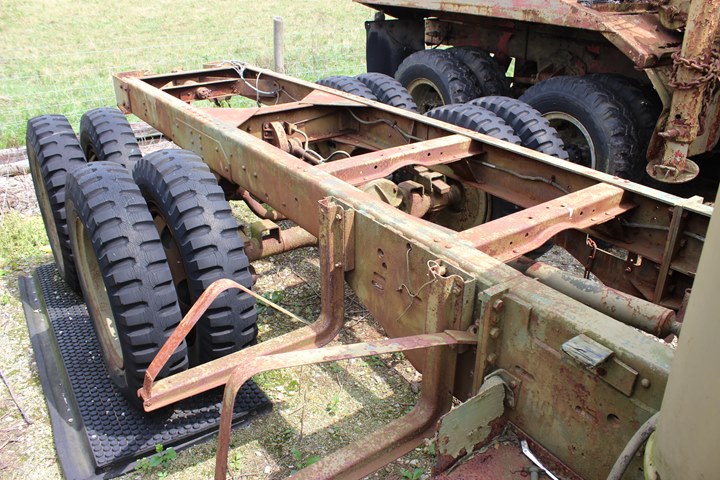

It can be identified as a CCKW-353 long bed
version because the fuel tank mounting bracket is on the side of the
frame. Author's Photo.
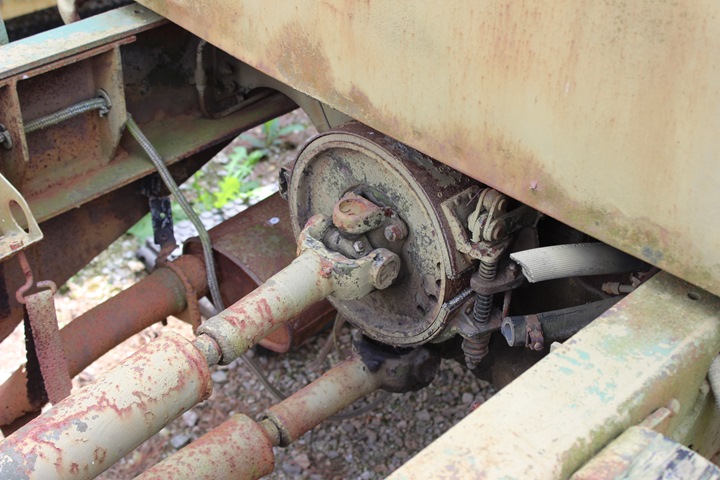

There are two drive shafts coming off the
transfer case. Author's Photo.
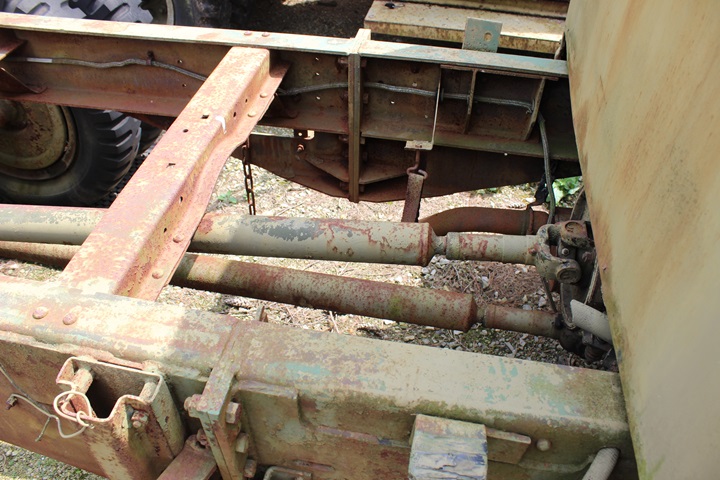

Author's Photo.
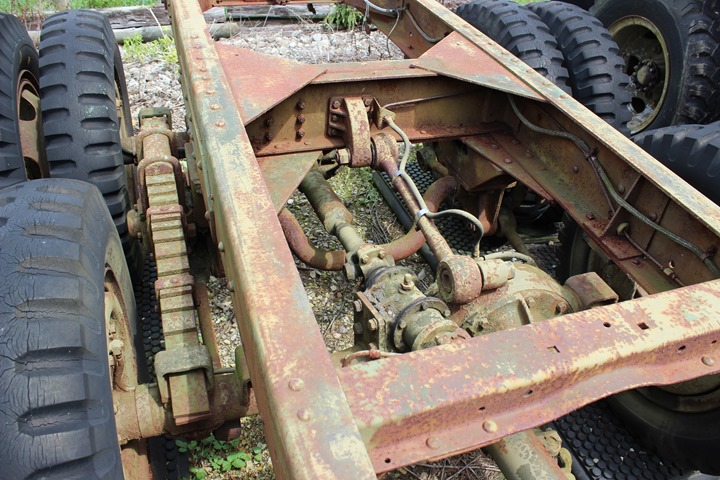

One drive shaft drives the first axle while
the other one continues to the rear axle. Author's Photo.
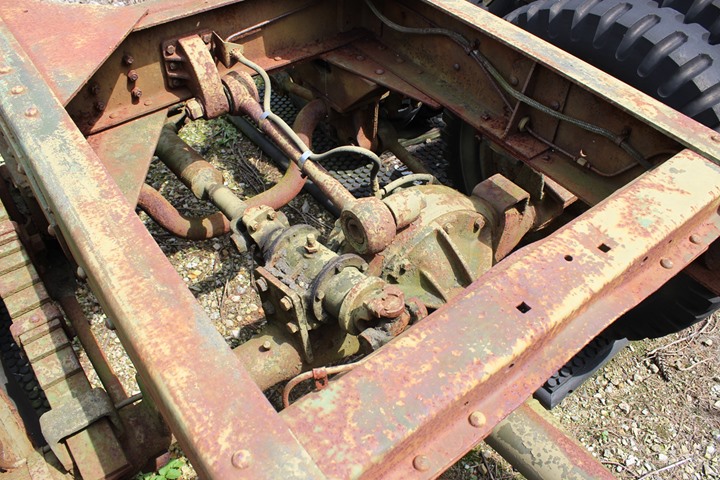

The axles and differentials for the truck were produced by
Chevrolet. Author's Photo.
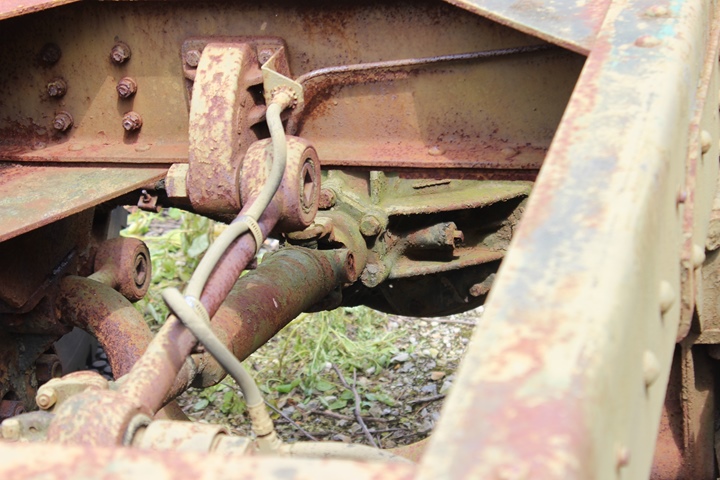

Author's Photo.
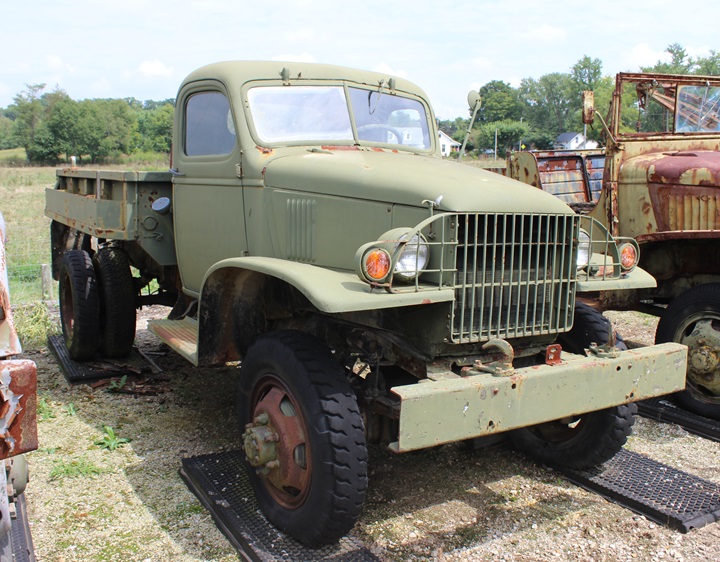
The Chevrolet-GMC Connection: Chevrolet was a significant
supplier to GMC during World War Two, along with building a considerable
amount of CCKWs and DUKWs at its St. Louis Plant.
Chevrolet supplied all of the closed cabs for
the GMC until the changeover to the soft tops in 1942-43. If one
looks at a Chevrolet or GMC truck with a closed cab from the front, it
can be difficult to determine which manufacturer made the vehicle.

This GMC can be identified as a GMC because of the rear dual axles.
Chevrolet only had one rear axle on its 1-1/2 ton trucks. On the
GMC, there are more side vents than the Chevy below. Looking
head-on, it is difficult if not impossible to distinguish between the
two. Author's Photo.

A Chevrolet 1-1/2 ton.
Author's Photo.

Author's Photo.
Derelicts: Unfortunately,
there are more than a few GMC trucks that have been left outside to
suffer the ravages of the weather.
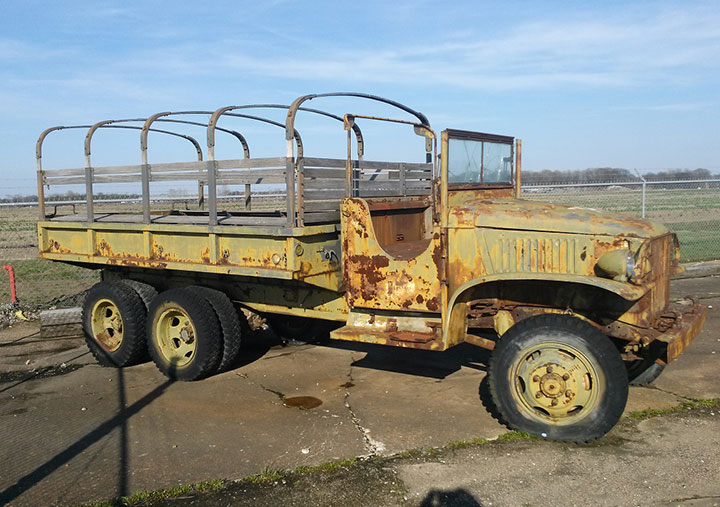

A CCKW-353 at the Halls, TN Veterans
Museum. The Museum has some very nicely restored vehicles on the
inside of the museum. Hopefully this is next on its restoration
project list. Photo courtesy of David Jackson, Jr.
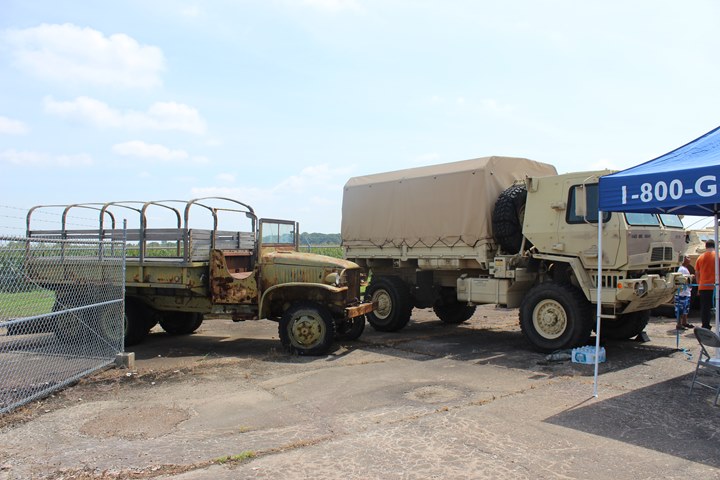

This photo was taken by the author at a later date than the previous
photo during the 2015 Halls Airshow to show the size difference between
the World War Two CCKW truck and the current M1078 Light Medium Tactical Truck.
Both are rated at 2-1/2 tons.
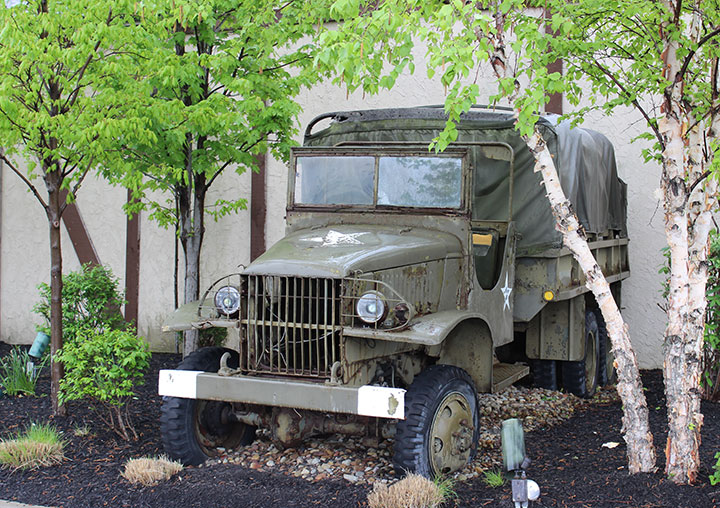

This CCKW-353 is on display outside at
the 100th Bomb Group Restaurant just north of the Cleveland Hopkins
International Airport. This truck has Timken differentials and
axles. Author's Photo.

Author's Photo.
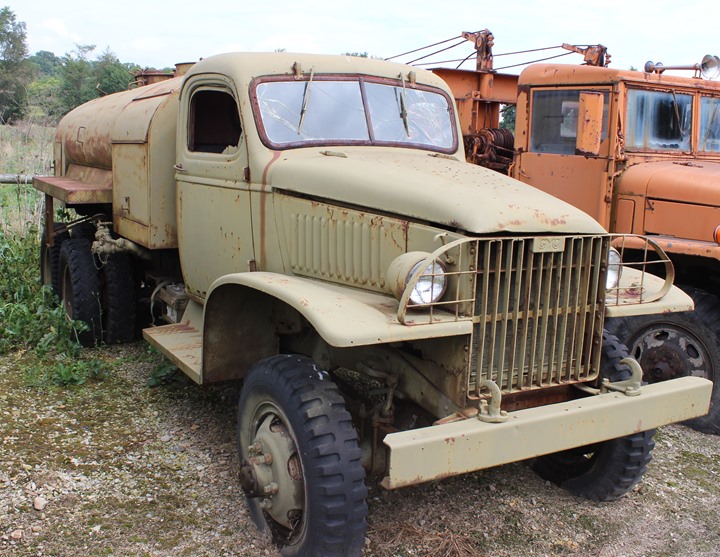

This CCKW tanker truck is at the Fort Economy Museum in Hallsville, OH.
Author's Photo.
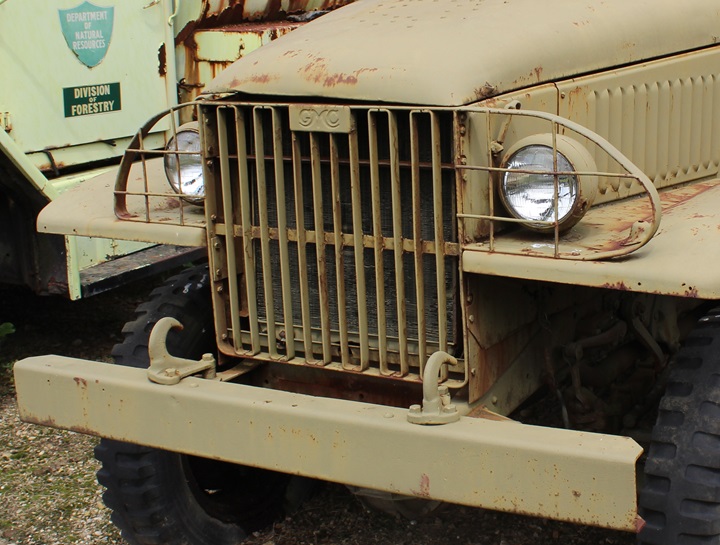

Author's Photo.
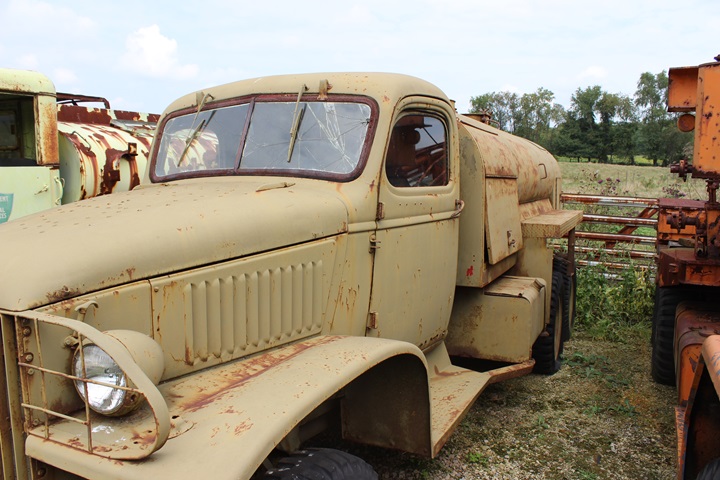

Note the separate mirror bracket making this
a post mid-1941 CCKW. Author's Photo.
Post World War Two:
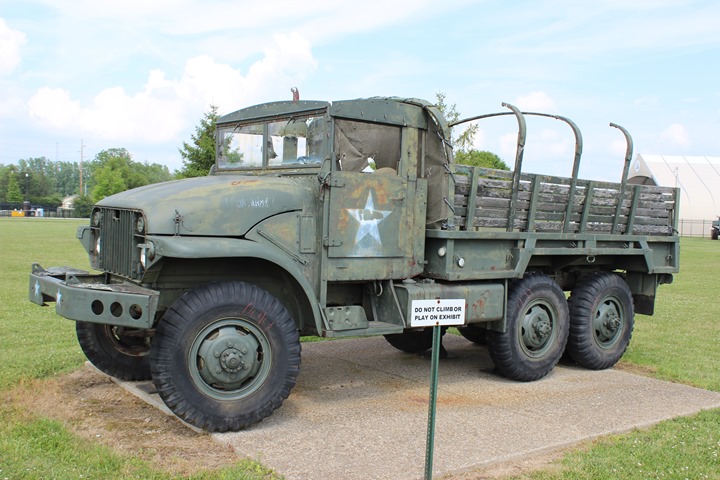

After World War Two GMC introduced M135 as its follow
on vehicle to provide a more up to date vehicle with the newest
technology for the US military. They were produced from 1951
through 1955 before being replaced by the REO designed M35 series.
This somewhat dilapidated M135 is on display at Camp Atterbury, IN. The
truck was originally supplied with a winch as the data plate shown below
indicates.
Author's Photo.
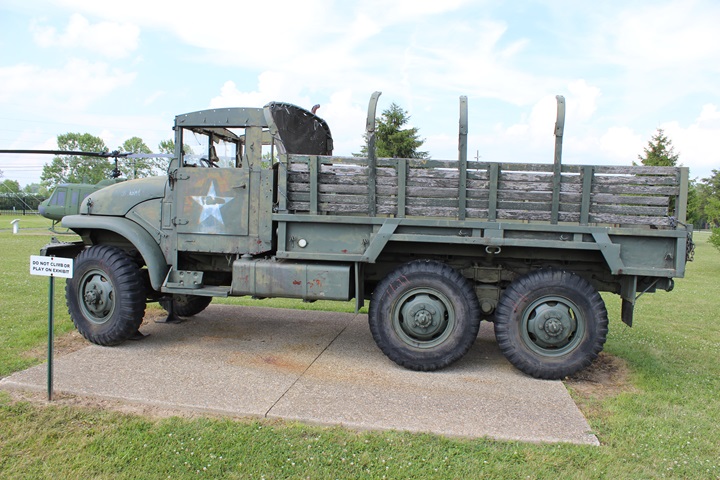

The M135 had several innovations over
the previous CCKW series which included a Hydra-Matic automatic
transmission, 24 volt electrical system, single large tires, and a sealed
waterproof ignition. There were other GMC trucks in the series
with other designations. Only the M135 had the single large tires. Author's Photo.

The M135 was delivered in July 1952
and has serial number 9758.
The first M135 came off the assembly line on September 13, 1951. A
total of 62,380 M135s were built by GMC. Author's Photo.
|


























































































































